The Task Manager was first introduced with Windows NT 4.0 and has since been a part of every Windows version and included in all editions. It is a powerful tool that gives you control over the running services and processes, as well as resource monitoring capabilities. Using the Task Manager, anyone who has access to your computer can change the affinity and priority for the processes, kill them, or even start new processes.
With just this information, it is safe to assume that the Task Manager is a powerful tool, and not everyone should be able to access it. Therefore, to increase your system’s security, it is advised to disable the Task Manager for certain users. The Task Manager is often disabled by sysadmins inside organizations so the end users are not able to perform any tasks they shouldn’t.
In this article, we show you how to disable the Task Manager or enable it if it has been disabled by your administrator.
Table of contents
Disable the Task Manager using Group Policy
The Group Policies are what the sysadmins control if your PC is part of an Active Directory. Of course, if your Task Manager is disabled by an admin, then the following method to enable it using the Group Policy Editor would not work. In this case, we suggest that you adopt the remaining two methods given below to activate the Task Manager.
If you have a standalone computer, then you may use the following steps to disable the Task Manager for a particular user. Note that you need to be signed in from that user account for it to apply to it.
-
Open the Group Policy Editor by typing in “gpedit.msc” in the Run Command box.
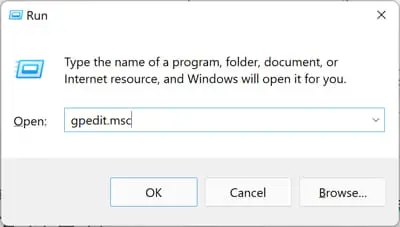
Open the Group Policy Editor -
Now navigate to the following from the left pane:
Local Computer Policy > User Configuration >> Administrative templates >> System >> Ctrl + Alt + Del Options
-
Double-click the policy “Remove Task Manager” on the right.
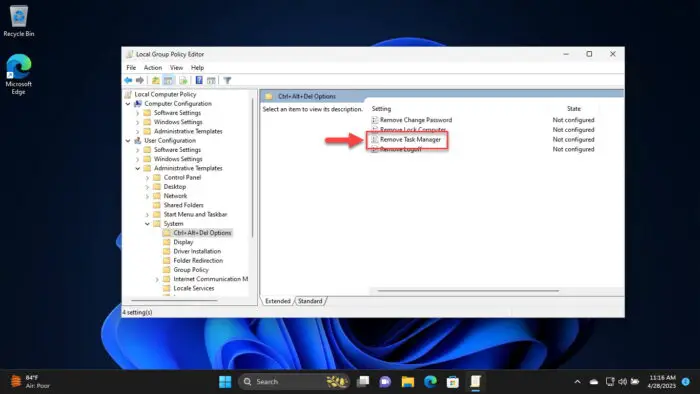
Open the Remove Task Manager policy -
Select “Enabled,” and then click Apply and Ok.
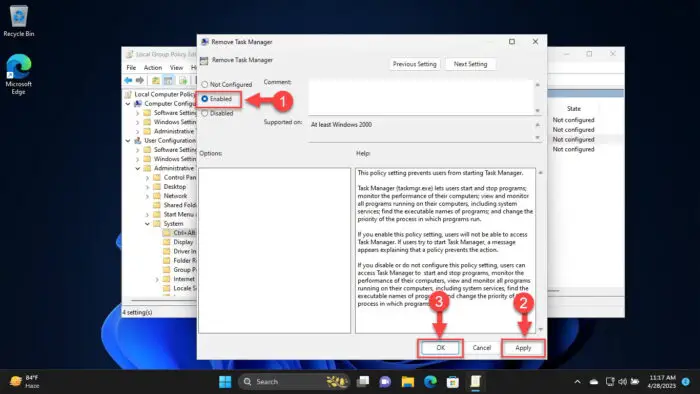
Enable the policy to disable the Task Manager Note that a restart or enforcement of the Group Policies would not be necessary.
The Task Manager will not be disabled. Any attempt to open the Task Manager will no longer work, and you will see a similar error message:
Task Manager has been disabled by your administrator.
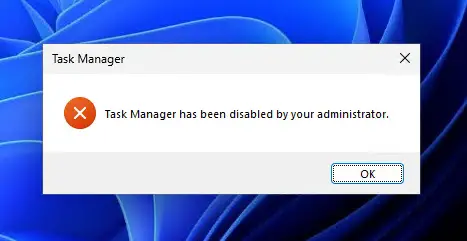
Remember that the Task Manager will only be disabled for the user account you are logged in from.
To re-enable it, all you need to do is set the Group Policy “Remove Task Manager” to either “Not Configured” or “Disabled.”
Disable the Task Manager from Windows Registry
You can also disable or enable the Task Manager from the Windows Registry. If your PC is part of a domain, then this is the method you should opt for.
Use the following steps to disable the Task Manager for the user account you are logged in from:
Note: Misconfiguration of critical values in the system’s registry could be fatal for your operating system. Therefore, we insist that you create a system restore point or a complete system image backup before proceeding forward with the process.
You can also use our top selection of disk imaging and backup software so you never lose your data or operating system again.
-
Open the Registry Editor by tying in “regedit” in the Run Command box.
Open the Registry Editor -
Paste the following in the navigation bar for quick navigation and hit Enter:
Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies
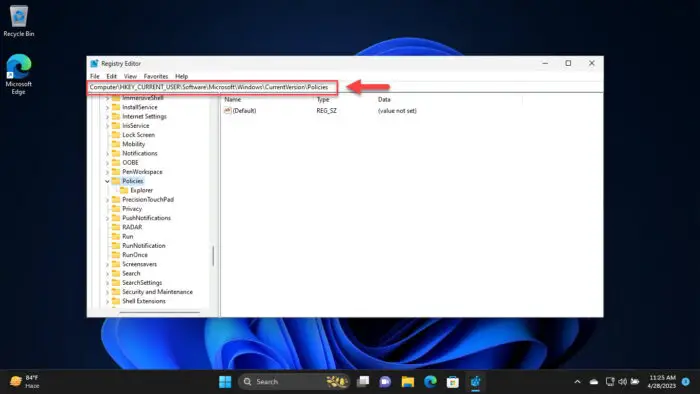
Navigate to the Policies key -
Right-click the “Policies” key, expand New, and then click “Key.” Name the new key “System“.
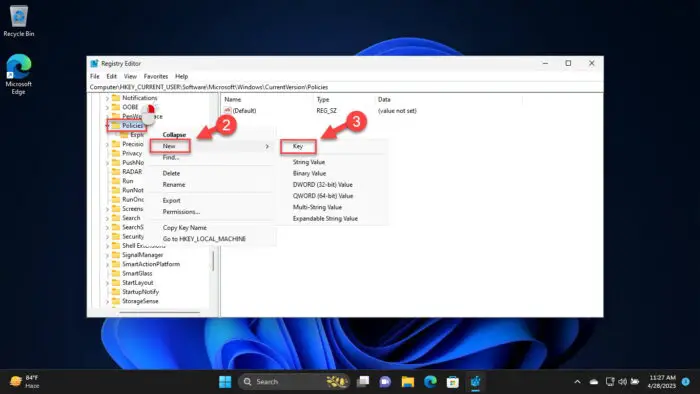
Create the new System key -
Right-click the “System” key, expand New, and then click “DWORD (32-bit) Value.” Name the new DWORD “DisableTaskMgr“.
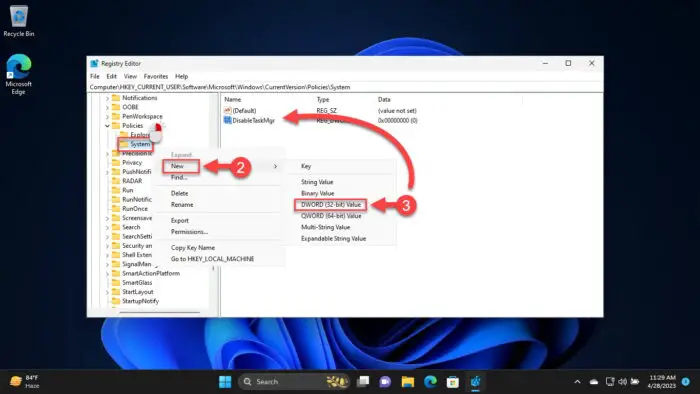
Create the new DisableTaskMgr DWORD -
Double-click the DWORD “DisableTaskMgr” and set its Value Data to 1.
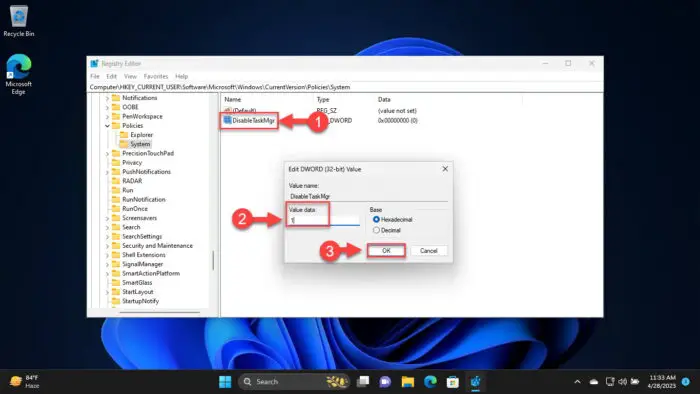
Disable the Task Manager from Windows Registry A system restart is not necessary for the changes to take effect.
As with the Group Policy method, the Task Manager will no longer launch.
In order to activate the Task Manager, all you need to do is change the Value Data for “DisableTaskMgr” from 1 to 0.
Disable the Task Manager using PowerShell (Command Line)
You can perform the same steps as above and disable or enable the Task Manager using a single command in PowerShell. This can also be applied to the Command Prompt or the Run Command box.
To disable the Task Manager using PowerShell, run the following command in an elevated PowerShell instance:
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f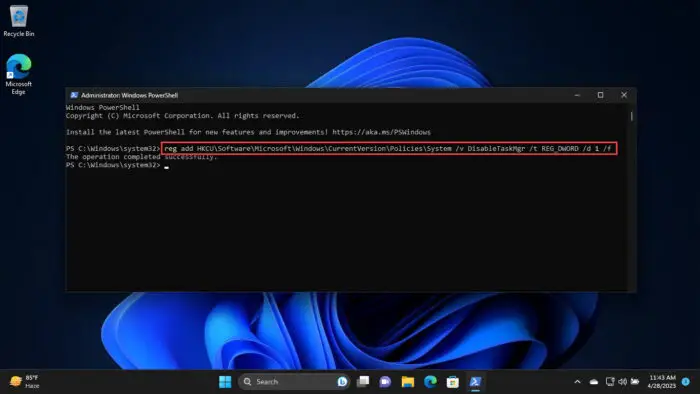
This command will make the same changes to the Windows Registry which have been discussed in the previous section above.
To re-enable the Task Manager, use the following command:
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /fThese are the methods you can use to enable or disable the Task Manager for specific user accounts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why isn’t my Task Manager opening?
The Task Manager may be disabled by your system administrator to prevent the end users from making any changes to the system processes. To enable the Task Manager, run the following in PowerShell:
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
How to disable the Task Manager using CMD?
You can use the following command in Command Prompt, PowerShell, or the Run Command box to disable the Task Manager:
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
To enable the Task Manager using cmd, use this command:
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f