Microsoft has released KB5014023 on the Release Preview channel for Insiders for Windows 10 21H2. The update does not include any new features, but includes a total of 27 fixes for the OS. It is anticipated that these fixes will soon hit the stable channel as well through an optional Type D update.
Alongside many significant fixes and improvements, upgrading your Windows 10 operating system to build 19044.1739 will significantly improve the transfer speed of the files and folders you copy to and from other partitions and external storage devices. Moreover, another issue has been resolved where a user’s PC may become entirely unresponsive if they signed out of their Microsoft OneDrive account.
Let us now see what other improvements are included and how to install this update.
Table of contents
Updates and Fixes
The following lists all the improvements made to KB5014023 for Windows 10:
- A new sorting version 6.4.3 has been introduced, which addresses the sorting issue that affects Japanese half-width katakana.
- Users are prevented from bypassing forced enrollment by disconnecting from the internet when they sign in to Azure Active Directory (AAD).
- An issue that could run an AnyCPU application as a 32-bit process has been addressed.
- An issue that prevents Azure Desired State Configuration (DSC) scenarios that have multiple partial configurations from working as expected has been fixed.
- An issue that affects remote procedure calls (RPC) to the Win32_User or Win32_Group WMI class has been fixed.
- An issue that occurs when adding a trusted user, group, or computer with a one-way trust has been fixed.
- An issue that fails to display the Application Counters section in the performance reports of the Performance Monitor tool has been addressed.
- An issue that might affect some apps that use d3d9.dll with certain graphics cards, and might cause those apps to close unexpectedly, has been addressed.
- A rare issue that prevents Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Outlook from opening has been addressed.
- A memory leak issue that affects Windows systems that are used 24 hours a day of the week has been addressed.
- An issue that affects the IE mode window frame has been fixed.
- An issue that prevents internet shortcuts from updating has been addressed.
- An issue that causes an Input Method Editor (IME) to discard a character if you enter the character while the IME converts previous text has been addressed.
- An issue that causes print failures when a low integrity level (LowIL) application prints to a null port has been addressed.
- An issue that prevents BitLocker from encrypting when you use the silent encryption option has been fixed.
- An issue that occurs when you apply multiple WDAC policies has been fixed.
- An issue that affects the behavior and shape orientation of a mouse cursor for Microsoft Defender Application Guard (MDAG), Microsoft Office, and Microsoft Edge, has been fixed.
- An issue that could cause the Remote Desktop client application to stop working when you end a session has been addressed.
- A reliability issue has been fixed in the Terminal Services Gateway (TS Gateway) service, which randomly causes clients to disconnect.
- Microsoft has deployed search highlights to devices that are domain-joined.
- An issue that displays the wrong image for the Input Method Editor (IME) mode indicator icon when you turn on the Font Mitigation policy has been addressed.
- The issue that causes a yellow exclamation point to display in Device Manager has been fixed. This occurs when a Bluetooth remote device advertises the Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP) source (SRC).
- An issue in which the Cluster Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) provider (ClustWMI.dll) generates high CPU usage in WMIPRVSE.EXE has been addressed.
- An issue that causes Microsoft’s deduplication driver to consume large amounts of non-paged pool memory has been fixed.
- The issue that causes file copying to be slower has been fixed.
- An issue that could cause the system to stop responding when a user signs out if Microsoft OneDrive is in use has been addressed.
- A known issue that could prevent recovery discs (CD or DVD) from starting if you created them using the Backup and Restore (Windows 7) app in Control Panel has been fixed. This issue occurs after installing Windows updates released on January 11, 2022, or later.
Many similar improvements had also been made earlier for Insiders on the Release Preview channel for Windows 11 with KB5014019
However, Microsoft did not disclose any known issues with the release. Let us now show you how to install this update.
How to Install Windows 10 Build 19044.1739 (KB5014023)
To install this update, you need to be running Windows 10 and subscribed to the Release Preview channel. If you have enabled Windows updates, you will automatically get a “New features are ready to install” prompt.
If not, follow these steps to install this update:
-
Open the Settings app, and then click Update & Security.
Open Update and Security Settings page -
On the right side, click Check for updates.
Check for pending updates -
The app will then scan for pending updates. When scanned, you will then see the following update available:
2022-05 Cumulative Update Preview for Windows 10 Version 21H2 for x64-based Systems (KB5014023)
It should then download and install automatically. Once it does, click Restart now to finalize the installation.
Restart your PC
Once the computer reboots, you can check that it has been updated to build 19044.1618 by typing in winver in the Run Command box.
Rollback/Uninstall Windows 10 Insider Preview Update
If you do not wish to keep the installed preview update for some reason, you can always roll back to the previous build of the OS. However, this can only be performed within the next 10 days after installing the new update.
To roll back after 10 days, you will need to apply this trick.
You can also resort to uninstalling the update using the method below.
Uninstall KB5014023 Using Command Prompt
Since we have installed this update using Windows Update, it will not be listed in the list of updates but you can see it in the command line, and thus uninstall it. Here is how:
-
Run the following command:
wmic qfe list brief /format:table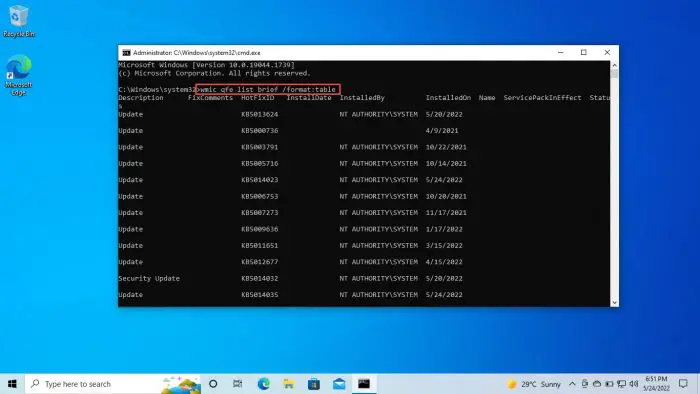
List installed updates -
This will show all the updates installed on the computer. Make sure that the update(s) you want to uninstall are on the list. Now run the following command to uninstall it:
wusa /uninstall /kb:5014023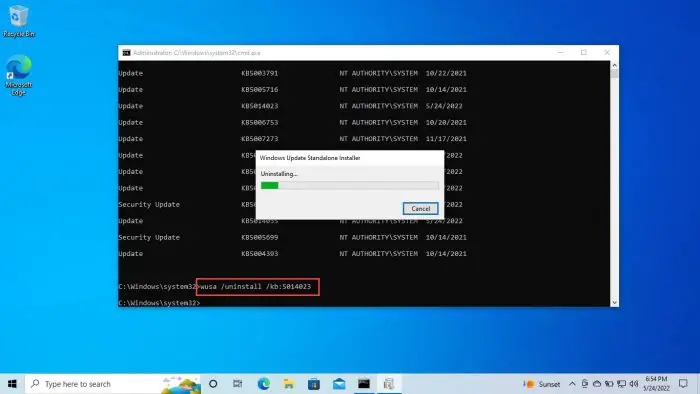
Uninstall update -
Now click Yes from the popup to confirm the action.
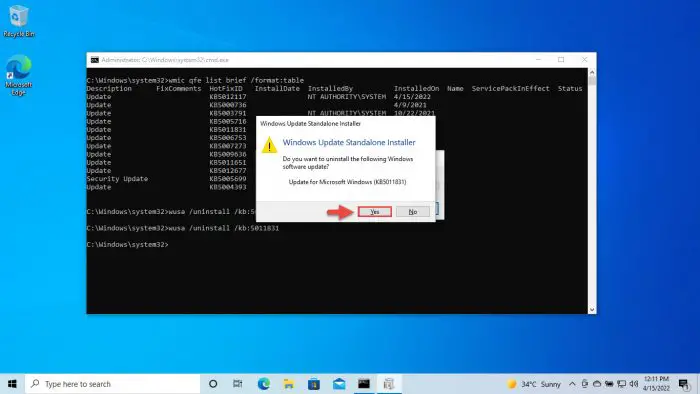
Confirm uninstallation -
The update will now begin uninstalling. When it completes, restart the computer for the changes to fully take effect.
Cleanup After Installing Windows Updates
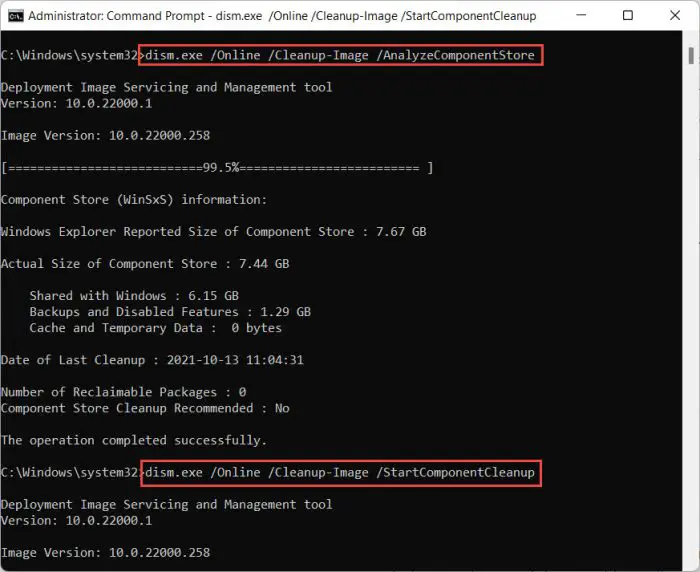
If you want to save space after installing Windows updates, you can run the following commands in Command Prompt:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /AnalyzeComponentStoreDISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanup