Is your PC starting to consume too much RAM? There might be a memory leak. Unnecessary high memory usage can cause problems for your PC, such as not being able to run the apps and programs that require that memory, or causing your PC to become slow and eventually even hang.
In this post, we are going to show you several ways you can fix this memory leakage on a Windows 11/10 computer. But before we do, it would be helpful to first understand what exactly memory leaks are.
Table of contents
What is a Memory Leak
System processes are temporarily kept in the RAM where they are executed, perform their respective tasks, and then once the task is completed, they free up the memory. However, an issue with the computer can cause a program to not vacate the memory once the task is completed. This phenomenon is known as a “memory leak”.
That said, a memory leak is entirely due to a software malfunction and has nothing to do with the hardware.
This unnecessary occupation of the RAM can result in problems for the computer and thus it is better to fix it. But how would you know if there is a memory leak, or if a process is just running several tasks and needs that much RAM?
There is no sure-shot way to determine whether a process is legitimately consuming your RAM or if there is a memory leak. The best indication of a memory leak is when you are running out of it. If you are unable to run the app because of less available memory, it may be possible that there is a memory leak.
In that case, here’s what you can do to fix it.
Fix Memory Leakage in Windows 11/10
Restart Computer
Since RAM is a volatile memory, restarting or shutting down your computer will erase all elements inside of it. Therefore, the most convenient method to free up RAM because of a memory leak is to reboot your computer.
When it reboots, you can see through the Task Manager that a significant portion of your system’s memory will be available to use.
Run Memory Diagnostics Tool
Windows comes with a preinstalled troubleshooter named “Windows Memory Diagnostic.” You can perform a memory test to ensure that there aren’t any bad sectors causing a memory leak.
To invoke a memory test, type in mdsched.exe in Run and hit Enter. In the pop-up window, click “Restart now and check for problems“.
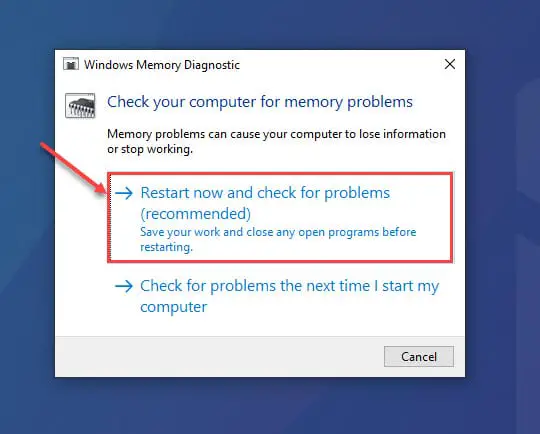
Your computer will now reboot and then automatically go into scanning mode. It will then scan your memory to look for issues with the memory. You can view the results in System Tray once the computer restarts.
Force Quit the Faulty Program
A malfunctioning software can is often the reason for a memory leak. If you find that a specific process is consuming a large chunk of your memory and suspect a memory leak, you can force-kill the process. Here is how:
-
Open the Task Manager using the CTRL + Shift + Esc shortcut keys.
-
In the Processes tab, right-click on the app/program you want to quit and then click End task from the context menu.

End task -
If prompted to send the data to Microsoft, click End task again to kill the program without sending data to Microsoft.
Now check to see if the memory has now become available to run the program that you want to. However, if it still hasn’t, it may be possible that a program scheduled to start up as soon as you log in is causing the leak.
Disable Auto Startup Programs
If you suspect that there is a memory leak as soon as you log into your user account, then there might be a problem with one of the auto-startup apps on your Windows PC. In that case, they will need to be disabled.
-
Open the Task Manager using the CTRL + Shift + Esc shortcut keys, and then switch to the Startup tab.

Switch to Startup tab -
Here, select the app causing a memory leak and then click Disable.

Disable auto-startup
Update Drivers
If none of the solutions above have worked for you, it may be possible that the memory leak is caused by a driver. In that case, you can try updating the drivers, or reinstalling them.
If you find any outdated drivers, we suggest you update them as the new drivers are more reliable and effective, and also enhance your system’s security through security patches.
Scan PC for Malware
It may be possible that your PC might be infected with malware that is eating up your RAM. It is best practice to fully scan your PC for any potential viruses and remove them.
Use the built-in Windows Security Antivirus (formerly Windows Defender) to scan your computer for malware. Here is how to do it:
-
Navigate to the following:
Settings app >> Privacy and security >> Windows Security >>Virus and threat protection
-
Here, click the Quick Scan button to perform a scan.
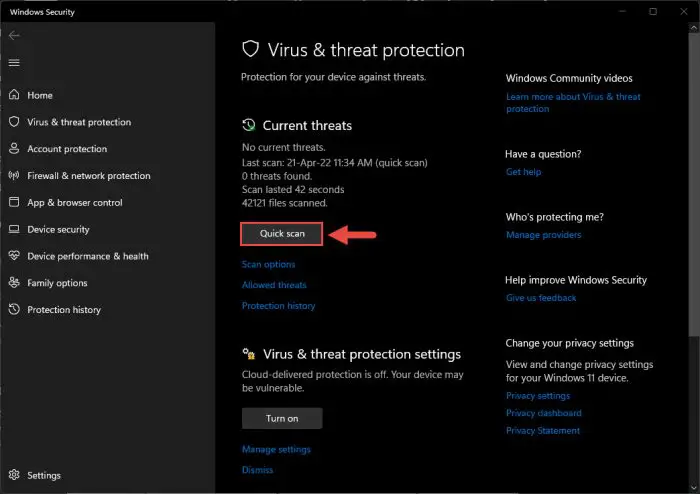
Perform quick scan Alternatively, you can also click Scan options below it to select a deep scan of your OS.
You can also perform a scan using a third-party antivirus. Here is a list of the top antivirus software to use to perform the scan. In case you are proceeding to purchase antivirus software, here are the 17 aspects you should always consider.
Disable SysMain Service (SuperFetch)
SysMain is a service in Windows 11/10 that is responsible for gathering information on what apps and programs you use, and how you use them so that Windows can be prepared the next time around and not take too long to load those apps. Of course, this service, while running in the background, can consume your memory.
Since it is not an integral Windows service, it can be disabled using the following method:
-
Open the Services console by typing in services.msc in the Run Command box.
Open the Services console -
Scroll down and right-click on the SysMain service. Click Properties from the context menu.
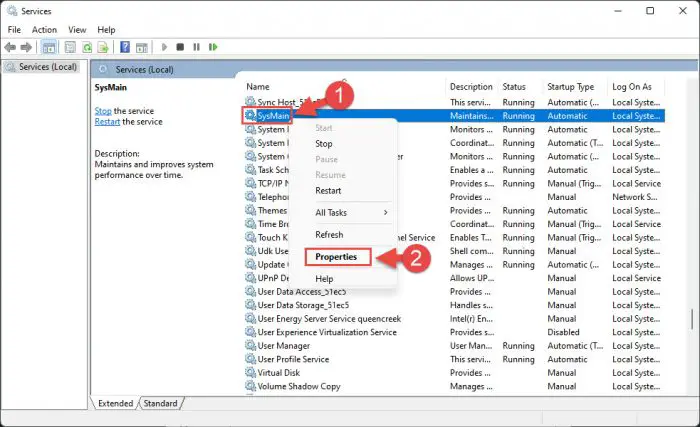
Open SysMain properties -
From the popup, select Startup type “Disabled,” click Stop, then click Apply and Ok.
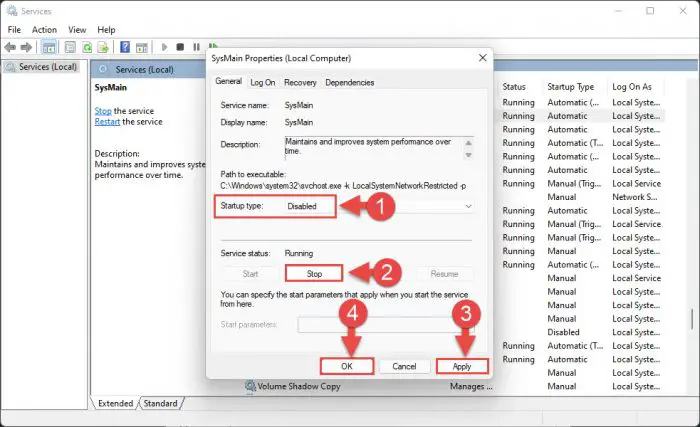
Disable SysMain
The service will now be disabled for good unless restarted manually.
Final Takeaway
Some might say that increasing your RAM may solve the problem of memory leakage, when in reality, it is not a solution, but only adding more available memory (at an additional cost), while some of it is still being wasted by software.
That said, the methods discussed to fix the issue in this post will hopefully help you in fixing its root cause.