When your computer is infected by malware, you may or may not be notified. It is also highly likely that you become aware of a cyberattack until it’s too late and the attackers have already gotten what they wanted.
With evolving technologies, the types and complexities of cyberattacks are also changing. Malware, or malicious software, is only one of the kinds of a cyberattack. There are also vast kinds of malware, each is designed to inflict a different type of harm and may also behave differently from the other.
That said, you never know when your computer or any digital device may be attacked by malware to inflict damage or provide financial gains to the attacker. Therefore, it is essential that you are always on your toes and wary of your cybersecurity environment.
We have already discussed the different kinds of cyber and malware attacks. In this post, we will only be discussing the best practices you can adopt to avoid malware before it has even infected your device or network.
If your assets are already compromised, learn how to remove malware instead.
The solutions provided in this article can serve as a checklist for regular home users as well as corporate users to keep their devices secure and safe from malware.
On this page
How to protect devices against malware – best practices
It is always better to be safe than sorry. This means that it is better to take measures to protect your devices against malware than get infected with malware and then spend both time and effort removing it.
While some practices can be applied to protect your devices against multiple types of malware, some are only specific to specific types. Therefore, it is recommended that you adopt all of the protection methods to ensure that your digital devices are protected at all times.
Whether you work alone or within an organization, you and all your colleagues should be educated about the different phishing tactics.
Phishing, or social engineering, is a method for attackers to obtain your personal or digital information. For example, they might send you links to malicious websites that pretend to be legitimate, so that you can enter your correct login details, which will then be available to the attackers.
Other social engineering examples include obtaining your Personal Identifying Information (PII), such as the name of your pet, your date of birth, etc. This information can be used to reset your password and bypass any security questions.
If you work for an organization or are in charge of digital security, then it is always better to provide all the staff training on digital security and awareness. Moreover, you can also conduct white-hat phishing techniques to run tests on your teams and ensure that everyone who fell for the trick gets more training.
Use secure authentication methods
Authentication mechanisms, such as passwords, keys, etc. are not only prone to physical security compromises but also to certain types of malware. For example, keyloggers can be used to communicate your passwords to the attacker. Therefore, you should use authentication methods that are even more secure.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a great method to add a layer of security. Even more so, Microsoft has included Passkeys for passwordless access to supported apps and websites. This feature is also available on your Google account, and pretty soon, more services will follow suit.
Additionally, you can also use biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, to make your authentication techniques even more secure.
One more thing to look out for is to never save your passwords on a device, or the network. For example, some people tend to create plain-text files to store all their credentials and other sensitive information. Instead, prefer using a secure password manager.
Keep OS and software updated
The operating system, may it be Windows, macOS, Android, or any other, must always be kept up to date. This means that you must install all system updates as soon as they are available.
Of course, there are exceptions when you do not install the update right away, such as when it includes significant known issues. Otherwise, it is always advised to upgrade the OS and all software installed.
OS and software updates normally include security patches. These patches fix known and zero-day vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited by attackers. Installing the updates ensures that the vulnerabilities no longer exist, thus your devices are protected.
Follow these paths in the respective operating system to check for pending OS updates. Install them if available.
-
Windows:
Settings >> Windows Update >> check for updates
-
macOS:
Apple menu >> System Settings >> System Settings >> General >> Software Update
-
Android:
Settings >> Software update >> Download and install
-
iOS:
Settings >> General >> Software update
In the case of other software, check out their manufacturer’s website or the app itself for updates.
Use non-administrative/standard account
All operating systems come with user accounts that have different privileges. In Windows, macOS, and Linux, there are both standard and administrative user accounts. The administrative, or the “root” account has the most advanced privileges. They can not only make changes to the software but to the system settings as well.
That being said, any malicious activity or operation performed from an administrative account can have tedious effects. Whereas, if the same activity is performed from a standard user account, the action may be automatically blocked because of insufficient permissions and privileges.
If you are not performing an activity that requires admin rights, it is recommended that you use a standard account instead. This reduces the risk of admin-level infections.
Use trusted antimalware
Antimalware, or as some prefer calling it antivirus is software that removes malware from your computers. Some advanced antimalware are complete suites that offer multiple security solutions under one roof. For example, BitDefender includes VPN, antivirus, internet security, and many other features.
While some reputed antimalware providers are paid, there are many free, yet unverified and new antimalware software on the market. People sometimes use these untrusted and free software thinking that their devices are now protected, whereas, it is quite the opposite.
Untrusted antivirus software usually does not protect your devices – they lack the basic security definitions that prevent zero-day attacks and exploits from impacting your PC. In some cases, some are even malicious antivirus software that only harm your computer further.
That is why, we recommend that you only use reputed and trusted antimalware to protect your devices to the full extent. This is an investment that is worth its reward.
Perform regular scans
You must perform deep scans of your devices to detect any malicious files or patterns.
Most reputed antimalware automatically detect malware as soon as they land on the PC, or are executed, and immediately quarantined. However, in some cases, a certain type of malware may go undetected, like fileless malware. In this case, a deep scan of the system can help root it out.
You can schedule a deep scan using your trusted antimalware software. If you do not have one, you can use the integrated Windows Security to perform a scan. Here is how:
-
Press the Windows Key + i to open Windows settings.
-
Go to the following:
Privacy & security >> Windows Security >> Virus & threat protection
-
Click “Scan options.”
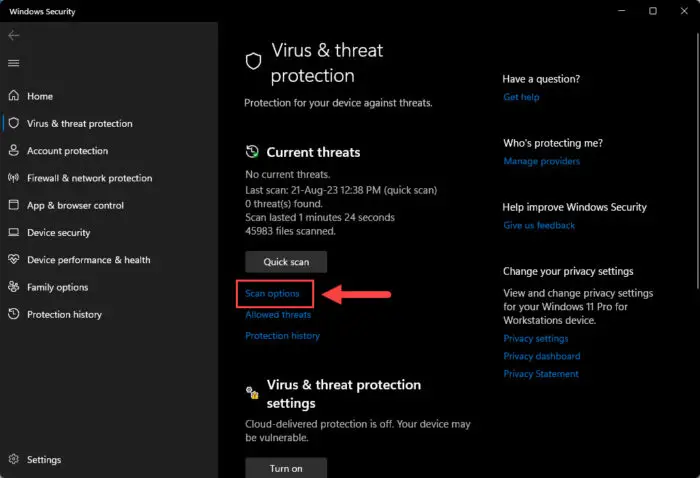
View Windows Security scan options -
Select “Full scan” and then click “Scan now.”
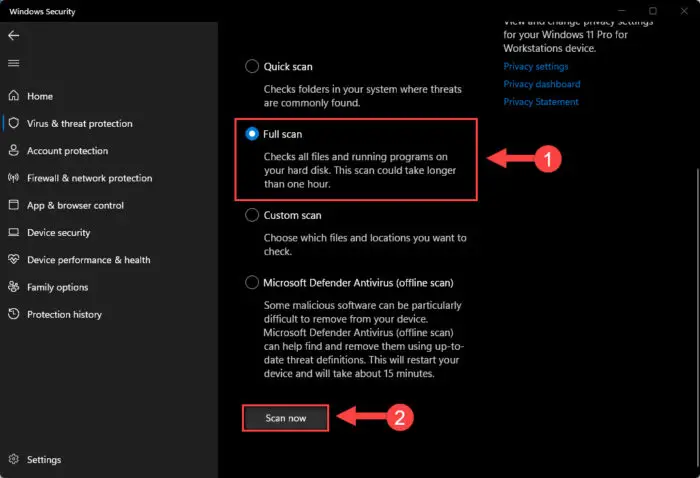
Perform full scan with Windows Security
On other operating systems, you can use their provided security software or use a reputed third-party antimalware software.
Avoid clicking malicious links and websites
As we will go ahead and learn, the most common method of spreading and delivering malware to a device is through spear-phishing emails and untrusted, compromised websites.
Normally, attackers use malicious emails to drop malware. They will make it seem like a legitimate email, and prompt you to either click a link or provide your personal information. Upon clicking the link, malicious software or code is downloaded and executed on your computer.
In other cases, some unmaintained and vulnerable websites have been compromised that inject malicious code into your PC without any interaction. This means that you do not even require to click anywhere on the web page – simply visiting the website is sufficient to plant the malware.
That said, you should look out for signs and reviews before clicking a link to determine whether it is legit or spam. Most phishing emails can be differentiated from legitimate emails if you look closely. It may have a weird sending email address, typos, informal layout, etc. However, do not solely rely on your wits as the attackers are getting smarter too.
This also includes downloads – whether from the internet or email attachments. Unverified downloads could also be malicious. Moreover, certain types of malware attach themselves to legitimate software. The software manufacturer may or may not be aware of the fact that their product has been compromised. Either way, this usually happens with legitimate software that is from unverified and unreputed vendors.
Avoid clicking popups
Popups are usually unwanted tiny windows that appear out of nowhere. These are usually found on websites and can contain any number of material, but normally contains ads. These ads could be legitimate, but often have inappropriate references and redirect you to another web page when clicked upon.
While there may be legitimate popups from the website themselves, most popups contain irrelevant advertisements that are trying to get you to accidentally (or deliberately) click on them.
Use encryption
Encrypting data ensures that it can only be unlocked and made human-readable using a private key that the encryptor holds. It secures your data and makes it less prone to theft and unauthorized access. Only if you hold the correct key can you access the information, once it is encrypted. This is what Bitlocker does on a Windows OS.
Regardless of what device you are using, or whichever OS, use data encryption so that it cannot be accessed if it ever falls into the wrong hands.
Learn how to turn on Bitlocker on Windows.
Avoid public networks
Public Wi-Fi networks are a great facility to have. You can have instant access to the internet at no additional cost. However, many do not realize just how dangerous those are.
Public Wi-Fi is unprotected, which means that anyone can connect to them. Attackers usually target such public networks, lurking for a potential target to connect to the device. They then fetch the device’s data and begin their attack, since they now have inside access to your device via the network.
Therefore, you should be wary of public networks, and try to avoid connecting to them wherever possible.
Adjust browser security settings
When using web browsers, most of us do not bother reviewing the default settings. We straight-up dive into browsing and downloading directly on the internet.
If you didn’t know, most modern web browsers have built-in security settings that allow you to harden it. This way, you can prevent cookies from tracking your online activity, automatically block popups, and reduce the attack surface for a malware attack.
Normally, the default security settings are mild. You can manually change these settings in the browser’s settings. For example, in Google Chrome, you can go to Settings >> Privacy and security >> Security, and select “Enhanced protection” to increase your web security to the maximum.
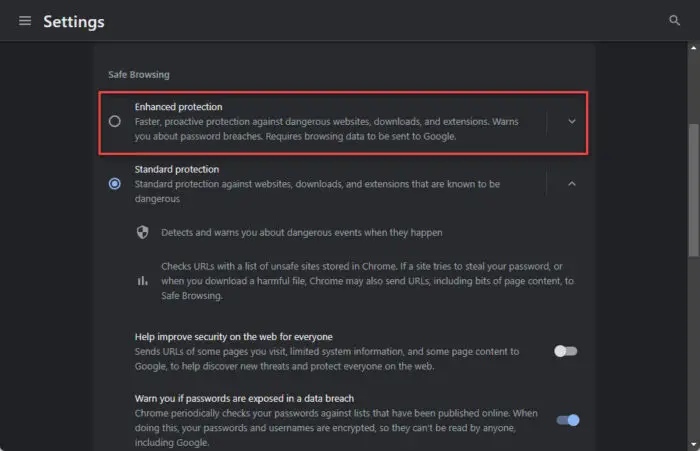
You can use the same concept on the web browser that you use to protect your devices against malware attacks.
Enable SmartScreen
If you are using Microsoft Edge as your web browser, then you should enable SmartScreen. SmartScreen provides on-the-go web security by scanning websites and downloading malicious files.
SmartScreen protects against phishing and malicious websites by automatically detecting and blocking malicious content. It uses a list of reported malicious software sites and programs known to be unsafe to crosscheck whether you have accidentally downloaded one. It also applies the same logic to files.
Use the following steps to enable SmartScreen in Microsoft Edge:
-
Open Microsoft Edge.
-
Click on the 3 dots in the top-right corner and then click Settings.
Open Edge settings -
Click “Privacy, search, and services” on the left.
-
Scroll down to the Security section and toggle the slider in front of “Microsoft Defender SmartScreen” into the On position.
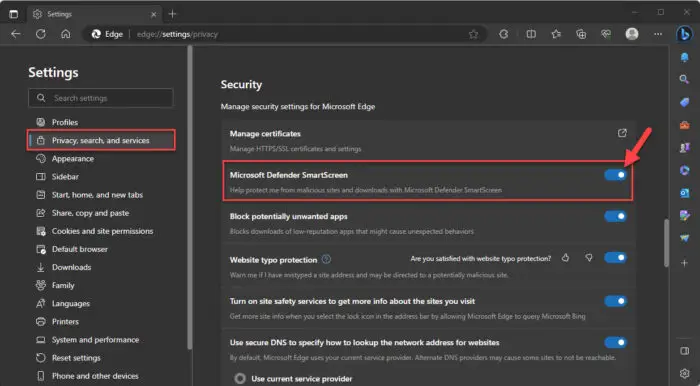
Enable Microsoft Defender SmartScreen
Enable Tamper Protection
Tamper Protection is a Windows Security feature. When enabled, this feature blocks malicious and third-party applications from making unauthorized changes to Windows Security settings and configurations.
Exploits and trojan horses increase the attack surface by reducing your system’s security by making changes to the current security settings. If Tamper Protection is disabled, viruses can take control of the app or its respective Group Policy or Windows Registry settings and make unauthorized changes, making your system vulnerable to other threats.
To enable Tamper Protection, use these steps:
-
Press the Windows Key + i to open the Windows settings app.
-
Go to the following:
Privacy & security >> Windows Security >> Virus & threat protection
-
Click “Manage Settings” under Virus & threat protection settings.
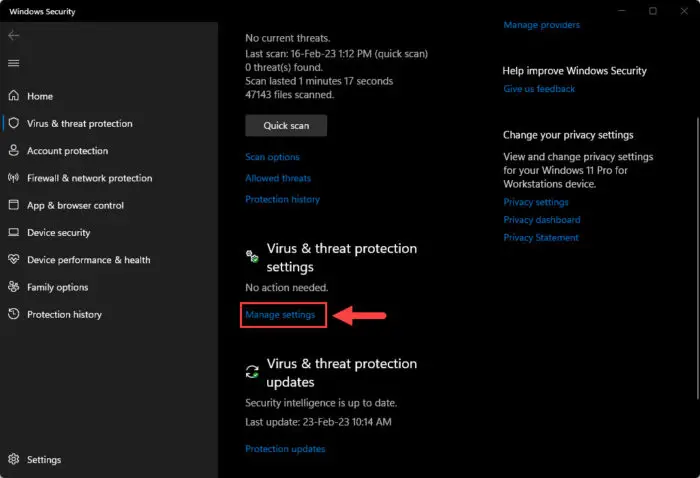
Manage virus and threat protection settings -
Scroll down and toggle the slider under “Tamper Protection” into the On position.
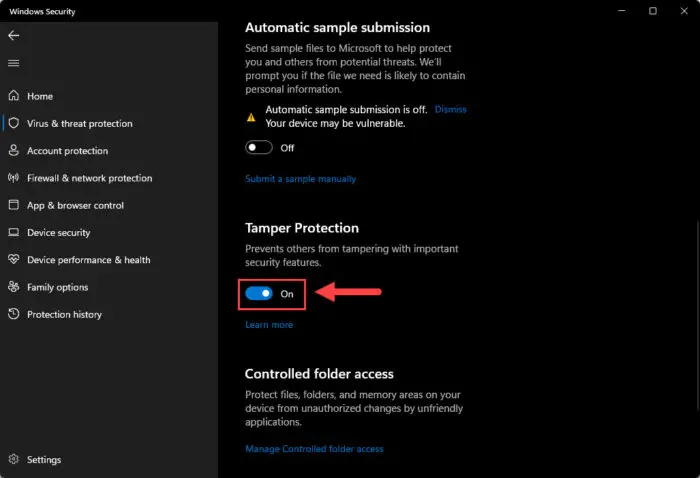
Enable Tamper Protection -
If prompted with a UAC, click Yes.
Do not connect untrusted storage devices
External storage devices, such as USB flash drives and external hard drives could potentially contain malware. Some malware even attaches itself to files that are shared via such storage devices. Therefore, it is recommended that you only connect the external storage devices that you trust and are aware of. Do not connect unknown devices.
Additionally, it is also recommended that you limit your file sharing. Do not copy files to and from your devices unnecessarily.
Change User Account Control (UAC) settings
User Account Control (UAC) is a Windows security feature that prevents the unauthorized execution of apps and processes with administrative privileges and also prevents malicious software from running on your computer. This feature has different settings, allowing you to completely disable it, or increase its level of security so that you are notified of every change to the system.
By default, the Windows operating system is configured at level 3 security (out of 4 levels in total), and set to “Don’t notify me when I make changes to Windows settings.” This is dangerous considering malware is executed from your account.
If you change this setting to “Always notify me when apps try to install software or make changes to my computer, or I make changes to Windows settings,” you will be notified even when software is installed in the background, from your account, without your consent.
To increase your UAC notification settings, use these steps:
-
Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “Control” and press Enter to open the Control Panel.
-
Go to the following:
System and Security >> Security and Maintenance >> Change User Account Control settings
-
Drag and drop the slider all the way up to “Always notify,” and then click Ok.
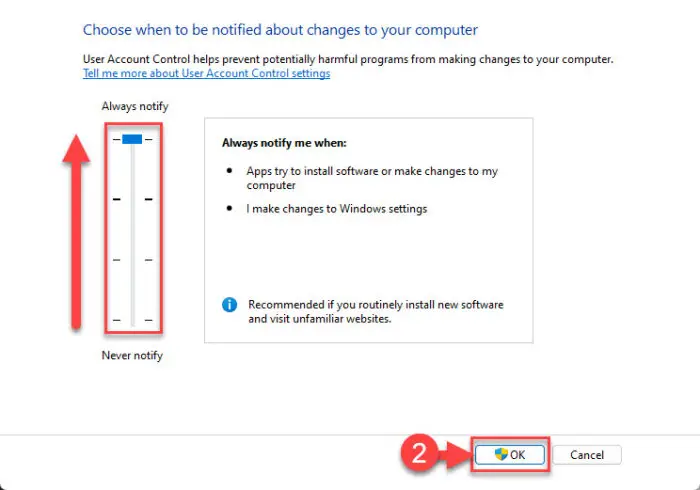
Increase UAC notification prompts
Increase internet security level
Other than browser and UAC security, Windows OS also has zone-level security. This means that you can change the security level of the internet.
By default, this setting is “Medium-high,” which allows you to download potentially unsafe content with only a warning, and is appropriate for most websites. However, changing it to “High” will ensure maximum safeguard and is appropriate for even harmful content.
To change the internet security level, use these steps:
-
Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “inetcpl.cpl” and press Enter to open the Internet Properties applet.
Open the Internet Properties applet -
Switch to the Security tab.
-
Select “Internet.”
-
In the “Security level for this zone” section, drag the slider to the top position.
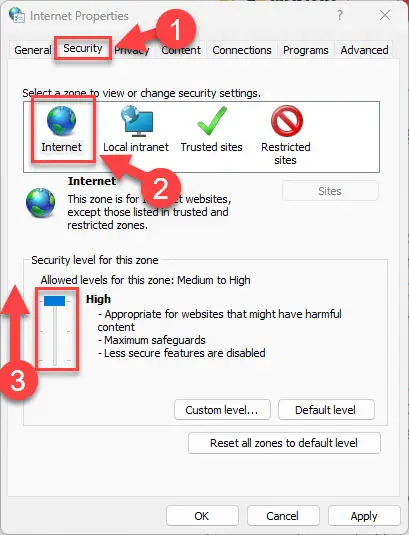
Increase internet security settings -
Now click “Apply” and “Ok” for the changes to take effect.
Enable/use firewalls
A firewall is a security system for networks that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. It manages data packets containing the sender and recipient’s IP addresses and port numbers.
Firewalls will make sure that your device(s) does not receive any unwanted traffic. Firewalls manage the data packages by either allowing or preventing them based on a predefined set of security rules. The purpose of a firewall is to prevent harmful traffic, such as viruses, prevent hackers from entering your internal network by creating a barrier between it and external sources like the Internet.
There are both hardware and software firewalls. We recommend that you use both. You can use Next-Gen Firewalls (NGFW) that include both Intrusion Detection Systems and Intrusion Prevention Systems to make your network as secure as possible. On top of this, you can also enable per-device firewalls.
Although the firewall is enabled by default on Windows, in case you had turned it off, here is how you can re-enable it:
-
Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “firewall.cpl” and press Enter to open the firewall applet.
Open Windows firewall applet -
Click “Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off” from the left of the window.
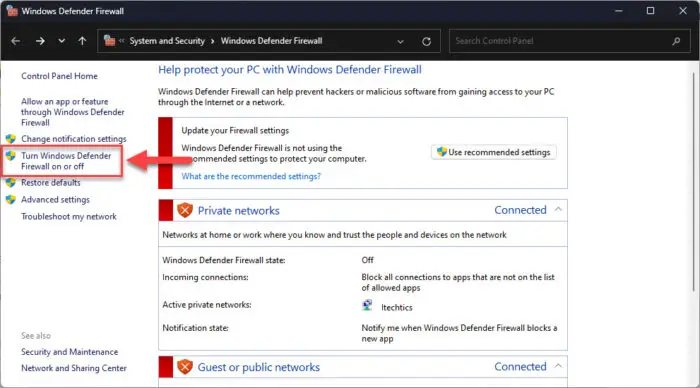
Enable or disable Windows Defender Firewall -
Now select “Turn on Windows Defender Firewall” for all network profiles and then click Ok.
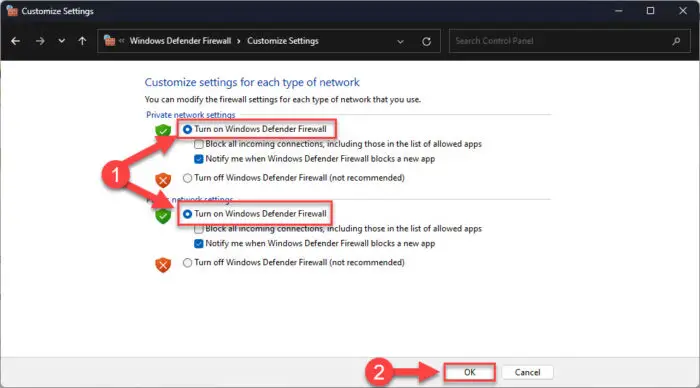
Turn on Windows firewall
Close listening ports
Ports are used by Windows services and applications to send and receive data over the network. If you wonder if this is what the IP address is used for, then you are absolutely correct. However, a unique IP address defines the path to a specific device, whereas a port defines what application or service on that particular device to send that information to.
Ports can be used by attackers to exploit and infect your device with malware. If you are not using a port, then it is highly suggested that you close them.
Before closing a network port, first, find all listening ports. Once you have determined which ports you want to close, use the following steps to get the job done on a Windows computer:
-
Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “firewall.cpl” and press Enter to open the firewall applet.
-
From the left side menu, click “Advanced settings.”
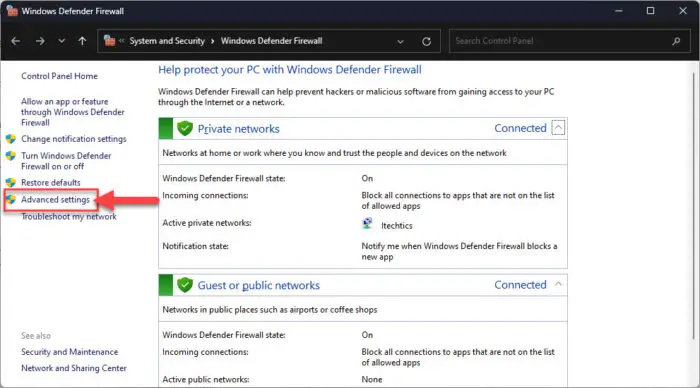
Open advanced firewall settings -
Select “Inbound rules” from the left pane, and then click “New rule” in the right pane.
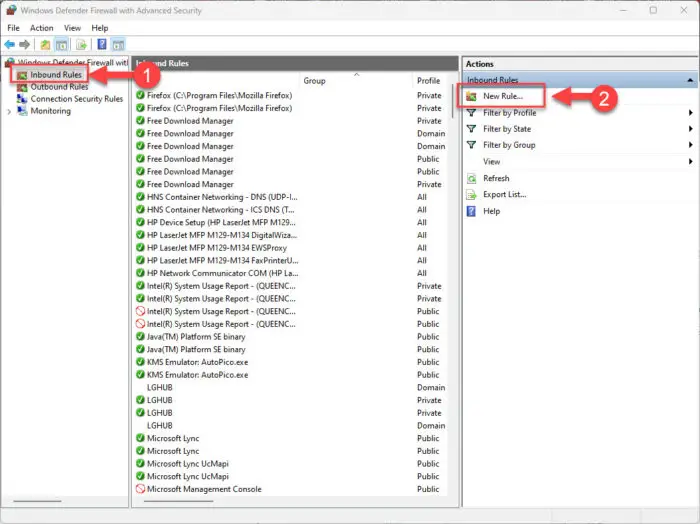
Create a new inbound rule The new rule wizard will now launch.
-
Select “Port” and then click Next.
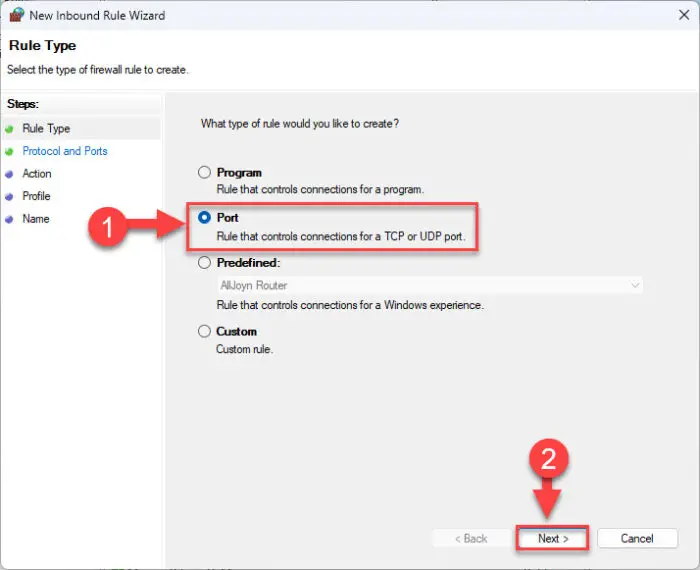
Create a rule for port -
Select the type of port (TCP or UDP), and then enter the port number you want to close in the field in front of “Specific local ports.”
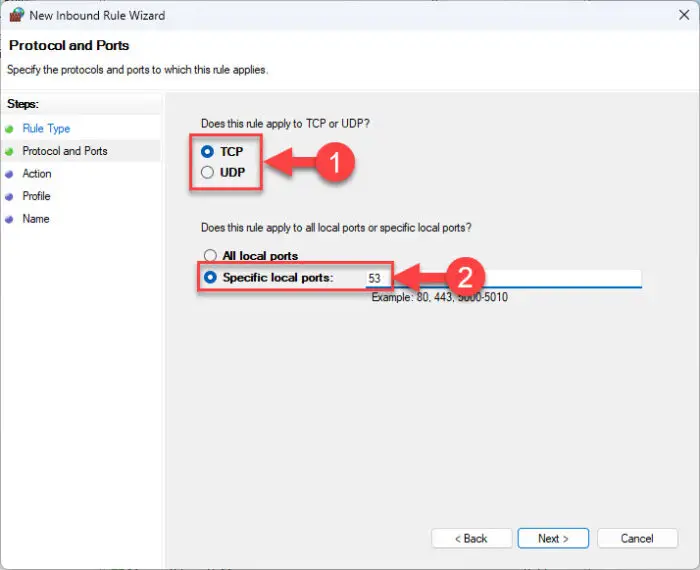
Enter port details You can specify more than one port separated by commas.
-
Click Next when done.
-
Select “Block the connection” and click Next.
-
On the Profile screen, select all profiles and click Next.
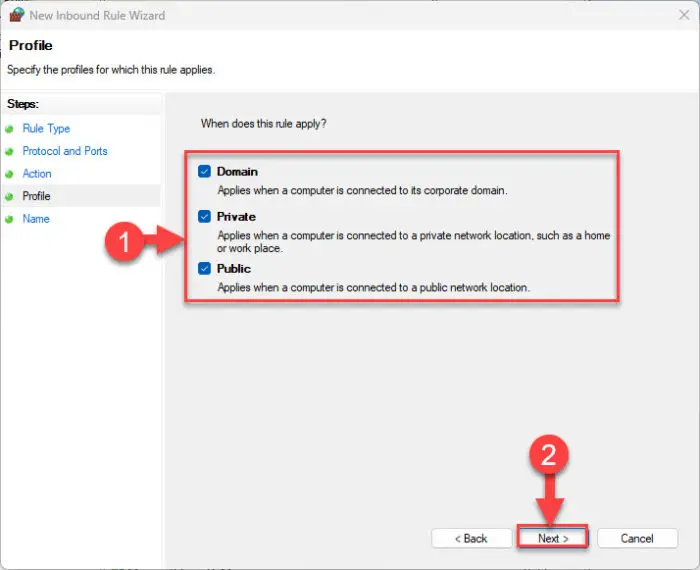
Apply rule for all network profiles -
Set a name for the rule and click Finish.
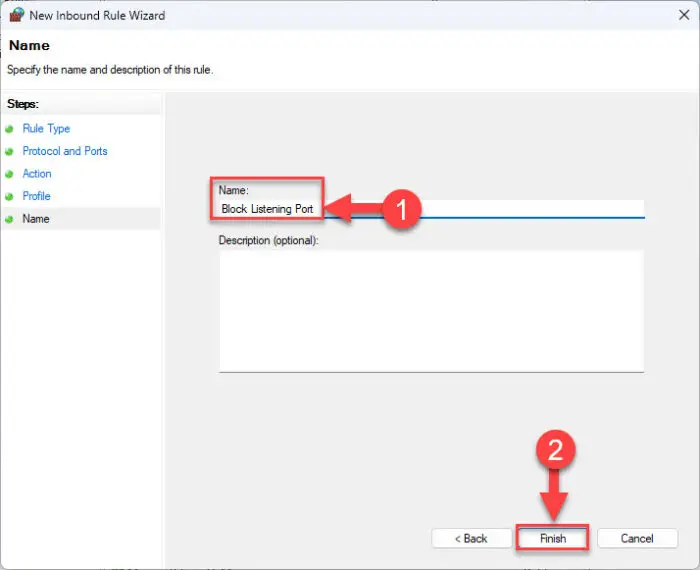
Block listening ports
The port(s) will now be disabled, and any exploits that may impact those ports should no longer have an effect.
Regularly backup data
Although backing up your data does not directly reduce the risk factor for a malware attack, it does however ensure business continuity by ensuring that your data is protected and available on demand.
There are multiple methods to back up your data across different operating systems. On Windows OS, you choose between File History and Backup and Restore, or create complete system image backups. Alternatively, you can also choose from one of our recommended disk imaging and backup software to make sure that you never lose your data again.
Reduce attack surface
Attack surface refers to the combined vulnerabilities within a network or an organization that could potentially be exploited.
When we talk about reducing the attack surface, it means hardening all possible assets and devices that could be a potential target for an attacker. This includes all possible measures – firewalls, monitoring, device security, account security, internet security, and so on.
One more practice that many organizations do is placing their most vulnerable assets, like database servers, behind DMZ proxy servers. This allows them to be off the grid and only allow access to authenticated devices and users.
Reducing the attack surface also protects you from botnet attacks, such as DDoS attacks.
Enable controlled folder access
Windows 10 and 11 come with a security feature called “Controlled folder access.” With is part of Windows Security and allows you to protect specific folders from ransomware attacks.
When controlled folder access is enabled, only trusted applications and programs can make changes to the folder. Thus, malware activities are automatically blocked.
Here are the steps to enable and configure controlled folder access:
-
Press the Windows Key + i to open the Settings app.
-
Go to the following:
Privacy & security >> Windows Security >> Virus & threat protection
The Windows Security app will now launch.
-
Scroll to the bottom and click “Manage ransomware protection” under Ransomware protection.
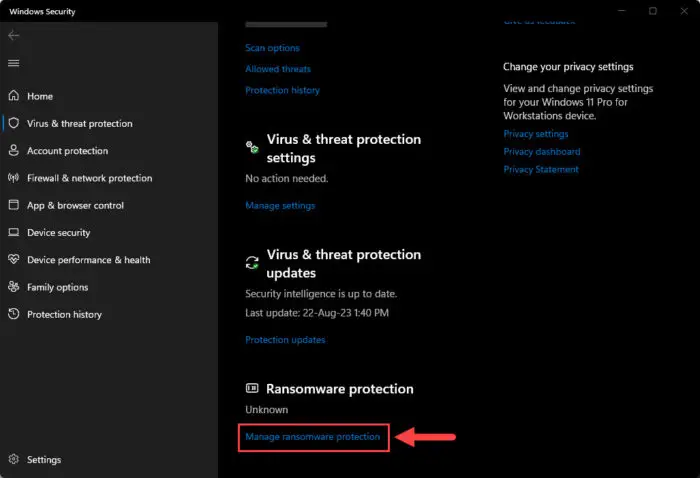
Manage ransomware protection -
Toggle the slider under “Controlled folder access” into the On position.
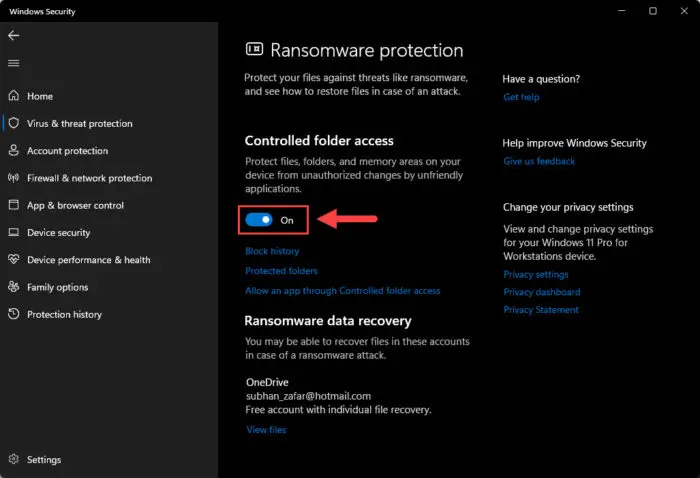
Enable controlled folder access -
If prompted with a UAC, click Yes.
-
Click “Protected folders.”
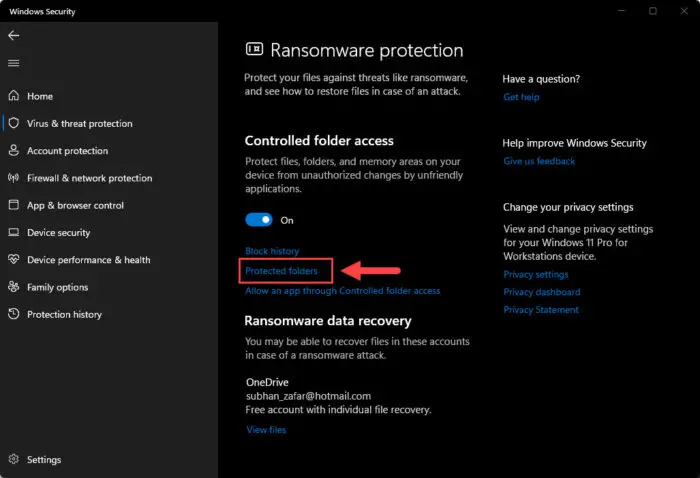
Manage protected folders -
Click “Add a protected folder.”
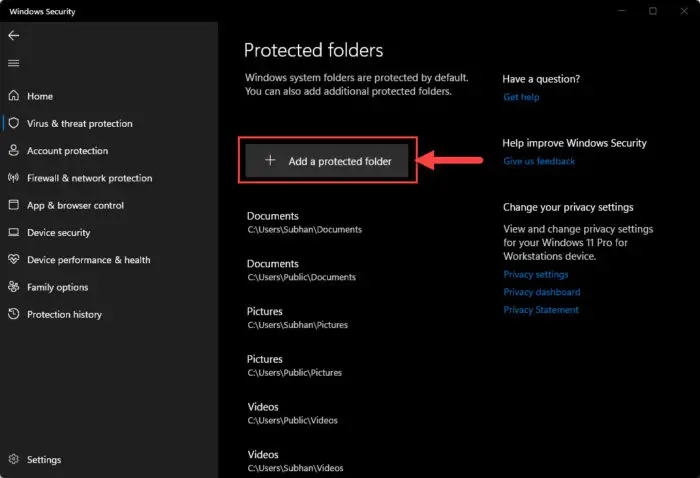
Add a new protected folder -
Now select the folder that you want to protect and click “Select folder.”
The folder will now be protected against untrusted apps and software that try to make changes to it.
You can repeat Steps 7 and 8 to include more folders to the Protected folders list.
Additionally, you can also click “Add an allowed app” to allow more apps to make changes to the protected folders. However, caution is advised while including more apps.
Use adblockers
Adblockers come as browser extensions as well as dedicated software that you can install on your device. The purpose of adblockers is to eliminate any annoying popups and banners that display ads. These usually work for web browsers where you see ads.
When the adblocker removes the ads, there are fewer chances for you to click on one.
You can find both free and paid adblockers for your specific browser on the internet. As a reminder, always use trusted and reputed software.
Purchase ad-free devices
Certain manufacturers include legal adware in the built-in OS and apps to compensate for the manufacturing costs. Although they may not be malicious, they can still redirect you to websites that could potentially deploy malware on your device.
Therefore, it is advised that you buy devices after doing homework on their OS and apps, and make sure that they do not include ads by default.
Cookies are one o the methods for tracking your online activity. Although these are used to remember your preferences and show targeted ads, they can be malicious if an attacker gains access to the information.
That said, be cautious while consenting to cookies and read the terms before allowing, if any, at all.
Monitor network traffic
Some malware attacks go undetected, such as rootkits. Even the most sophisticated antimalware software is sometimes unable to detect and quarantine rootkits. Therefore, you should also employ constant network monitoring to prevent rootkit attacks.
Monitoring and alerting techniques can point out unusual network activity which is based on behavior. Even if an ongoing rootkit attack goes undetected, network monitoring can catch it midway without letting it inflict too much damage.
If you do see unusual network activity while monitoring network traffic, it is advised to immediately disconnect the target device(s) and take them offline.
Use honeypots
Literal honeypots are used to attract bees. In the digital realm, a honeypot refers to something that attacks the attackers on purpose. Although this approach does not directly mitigate malware attacks, it can be used to keep your actual data safe and secure.
Honeypots are normally planted by large organizations whose purpose is to lure attackers in case of a breach. The attackers then waste time infiltrating such honeypots that contain fabricated information designed to look legitimate. Meanwhile, the actual assets of the organization remain unharmed, while the security professionals have sufficient time to react to the breach.
Increase network bandwidth
Having ample bandwidth is crucial, especially if you want protection against DDoS attacks.
You cannot protect your end devices from DDoS attacks. If an attacker wishes to use botnets for an attack, they will most likely clog up your bandwidth and cause disruption. However, if you have sufficient bandwidth to spare, you can continue with your tasks whilst a DDoS attack is taking place.
Employ a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN’s primary purpose is to distribute the server’s traffic across different locations. However, some CDNs, like Cloudflare, also provide other security services, such as bot management, DDoS protection, etc.
Moreover, they also offer SSL certificates that ensure that the traffic to and from your server is secure and protected.
Use Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Unnecessary access permissions should be avoided at all costs. When someone does not need access to certain assets, they should be revoked immediately. This means that they should not be allowed to poke in areas that do not concern them.
Restricting access through ACLs is perhaps the best method to limit unauthorized access for attackers, as well as malware deployment. Therefore, use ACLs wherever possible and do not grant access to users and devices where they shouldn’t be.
Takeaway
Malware, or malicious software, is not only of one kind. Attackers modify and manipulate malware to their advantage, and make them sophisticated enough to be untraceable even by the most advanced antimalware programs. This is why it is better to protect against malware than remove them from your devices after it has been compromised.
In this article, you shall find all the possible solutions to adopt while ensuring that your devices are safe and protected against malware attacks. Even so, note that they are still not 100% protected, since attackers can still find a vulnerability and exploit it to gain unauthorized access and deploy malware.
Moreover, this article also covers the best practices for organizations and individual users to protect themselves from phishing and social-engineering techniques, and keep their personal information private.





