A cache, regardless of its type, is where temporary files are stored for quick access. This technique is applied by an app or program to fetch information swiftly. This approach reduces the load on the medium, whether its system resources or the internet bandwidth and makes the operations quicker.
The memory on your computer also stores temporary cache data, which is known as RAM or Memory Cache. Although it is created to reduce the operational stress on the applications, by quickly fetching and processing the data directly inside the memory, it also has its caveats. The drawback of memory cache is it leaves little space for processing data by apps running in the foreground. This results in a slow-running computer.
This is why you occasionally need to clear the memory cache to allow the processing of the more important tasks.
In this article, we discuss how the memory cache works, and the different ways you can clean it.
This Page Covers
When to Clear Memory Cache
The cache stored inside your system’s memory is independent and has no direct effect on your computer. Usually, it is small in size, relative to the overall size of the available memory capacity. The applications and programs on your computer create these caches for quick processing – the memory itself does not need a cache.
However, when the cache size has increased significantly, it can cause your computer to lag. You will experience longer processing times and poor performance. These are the symptoms of when you might need to clear out the memory cache. But these are assumed symptoms.
Memory leaks can also cause increased memory caches.
To be sure of when to clear out the memory cache, you should find the current value of the memory cache. Use the steps in the following section to find out the size of your memory cache.
Learn how to clear all sorts of cache on Windows.
How to Check Memory Cache Size
To check your current memory cache size, use these steps:
-
Open the Task Manager and switch to the Performance tab.
Open the Performance tab in Task Manager -
Click on the “Memory” tab.
Open the Memory tab in Task Manager -
Here, you will find the memory cache size under the Cached heading.
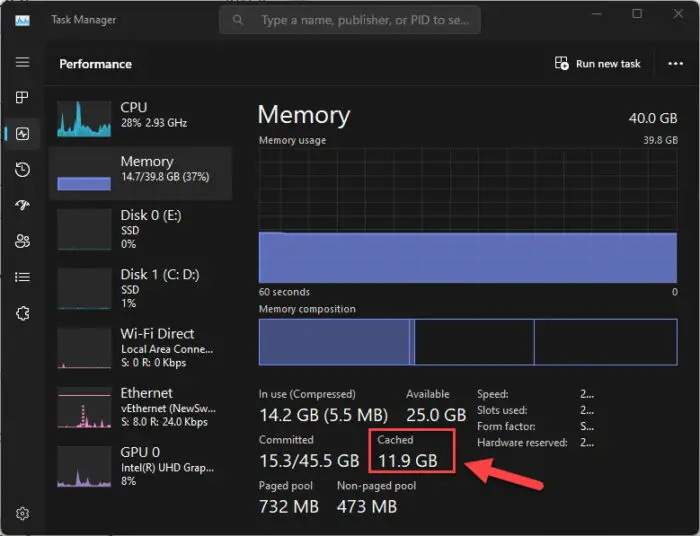
Find the memory cache size
As you can see from the image above, the memory cache is significantly large, around 12 GB. It is definitely due to a cache cleaning.
Let us now show you the different methods to clear the memory cache.
Clear Memory Cache
Restart the Computer
The easiest way to clear the memory cache is by restarting the computer.
RAM is a volatile memory, which means that it loses all data as soon as it loses power. Therefore, restarting the computer gets rid of all the data on it, including the memory cache.
When the compute reboots, you will notice that the memory cache (from the Task Manager) is reduced and negligible.
Manually Flush Memory Cache
The easiest way to clear the memory cache is to flush it. It can be done using a simple shortcut that you can create on your desktop. Here is how:
-
Right-click on a blank space on the desktop, expand New and then click Shortcut.
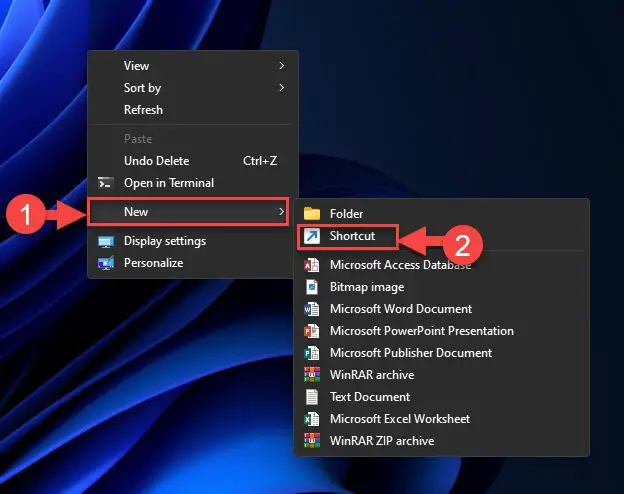
Create a new shortcut on the desktop -
In the Location field, paste the following and click Next.
%windir%\system32\rundll32.exe advapi32.dll,ProcessIdleTasks
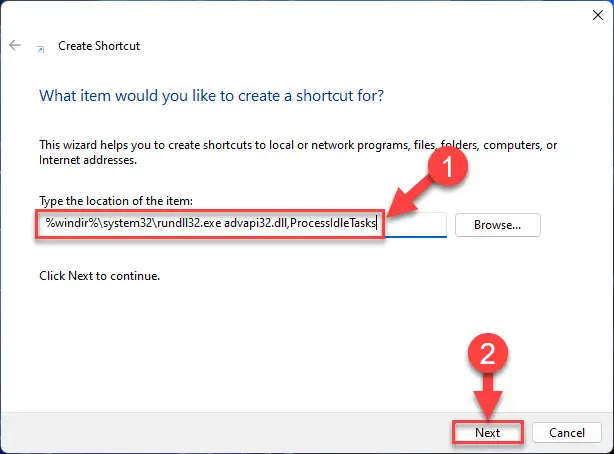
Enter the shortcut path -
Set a name for the shortcut and click Finish.
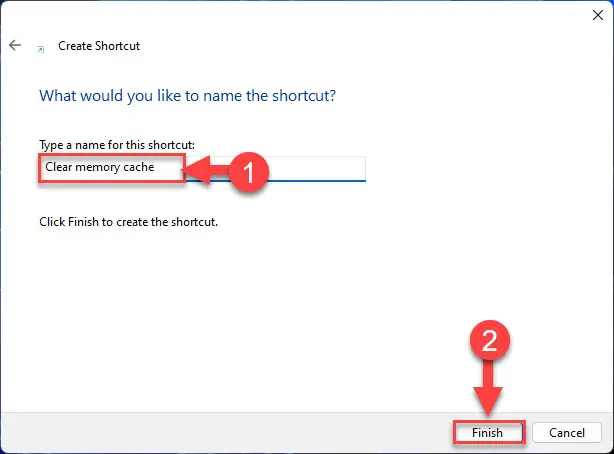
Name the shortcut -
Once the shortcut is created, run it to dump the cache.
You can then use this shortcut when needed to flush the memory cache.
Close RAM-Hungry Background Applications and Processes
The applications and processes that create the most memory cache are also the ones that consume the memory the most. Therefore, to clear the memory cache, kill the tasks and processes that consume the most memory.
To close any processes consuming system memory, open the Task Manager and switch to the Processes tab. Click on the “Memory” column header to sort the processes in descending order, and then kill the apps/processes that you do not need.
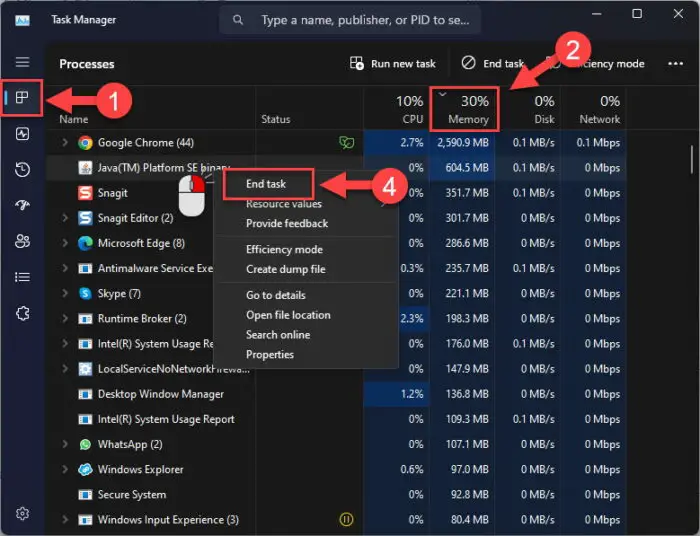
If you end most of the tasks, you will notice that the memory cache will be near to negligible. However, if you only end some of the apps and processes, it will only reduce the size of the cache.
Disable Startup Programs
In the Windows operating system, some apps and programs are set to start up automatically, in the background or the forefront, as soon as you sign into your account. These apps contribute to the memory cache, and disabling them will clear it up.
Use the following steps to disable the startup programs:
-
Open the Task Manager and switch to the “Startup Apps” tab.
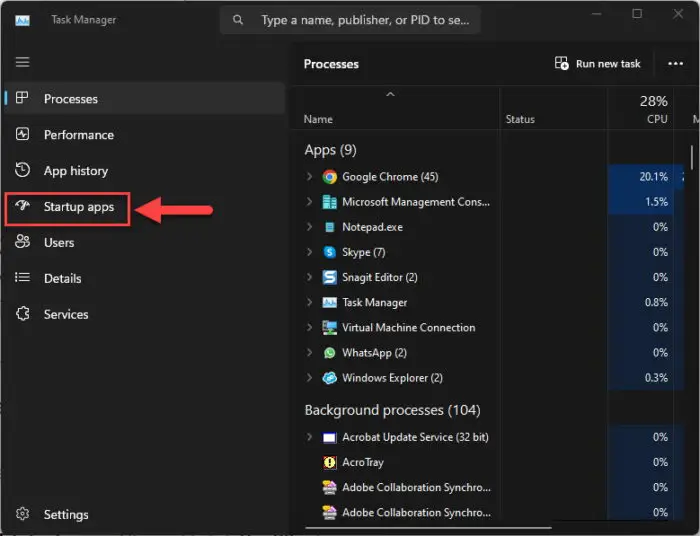
Open Startup Apps in Task Manager -
Right-click the apps that are enabled and then click “Disabled” from the context menu.
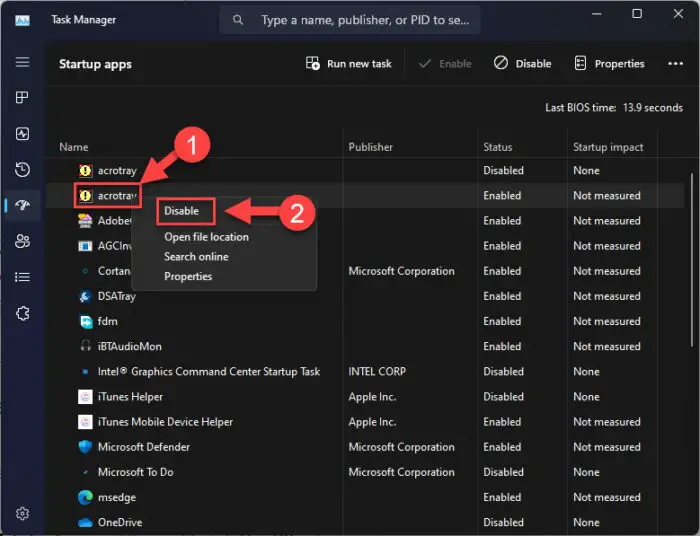
Disable startup application -
Repeat the step until all non-essential apps are disabled.
Adjust PC for Best performance
There are plenty of animations and other insignificant effects in the Windows OS that create a memory cache. Disable them and optimize your PC for best performance by performing the following steps:
-
Open the System Properties applet by typing in “sysdm.cpl” in the Run Command box.
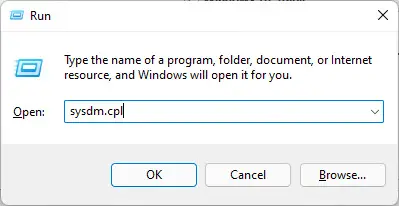
Open System Properties applet -
Switch to the Advanced tab and then click “Settings” under Performance.
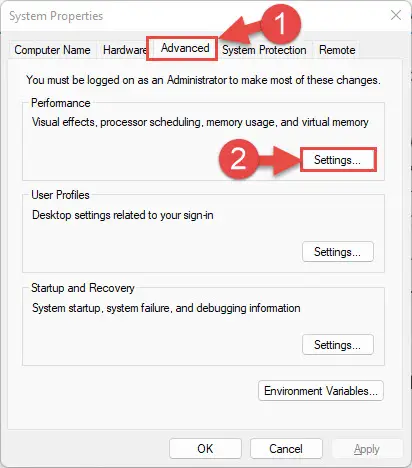
Open advanced settings -
From the pop-up window, select “Adjust for best performance,” then click Apply and Ok.
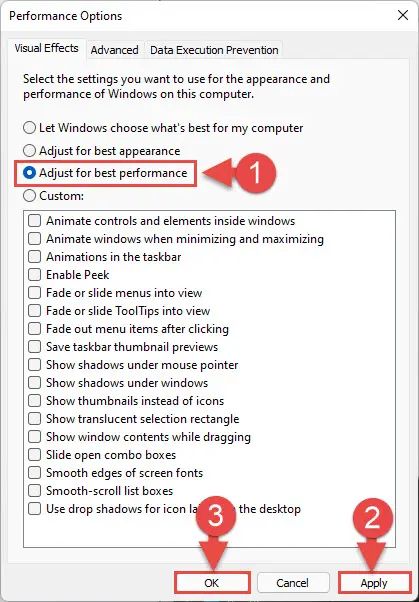
Adjust visual effects for the best performance -
Now restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
Once the computer restarts, the visual effects will be automatically turned off.
Clear Pagefile when Shutting Down
Pagefile is a hidden system file on your hard drive that is primarily there to compensate for low RAM. When the computer shuts down, the memory cache is cleared, but the Pagefile remains, which also contributes to the memory cache when the computer boots back up again.
You can configure the Pagefile to clear automatically whenever you shut down the computer. Here is how:
Note: This process involves making manual changes to the Windows Registry. Misconfiguration of critical values in the system’s registry could be fatal for your operating system. Therefore, we insist that you create a system restore point or a complete system image backup before proceeding forward with the process.
You can also use our top selection of disk imaging and backup software so you never lose your data or operating system again.
-
Open the Registry Editor by typing in “regedit” in the Run Command box.
Open the Registry Editor -
Paste the following in the navigation bar for quick navigation:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management
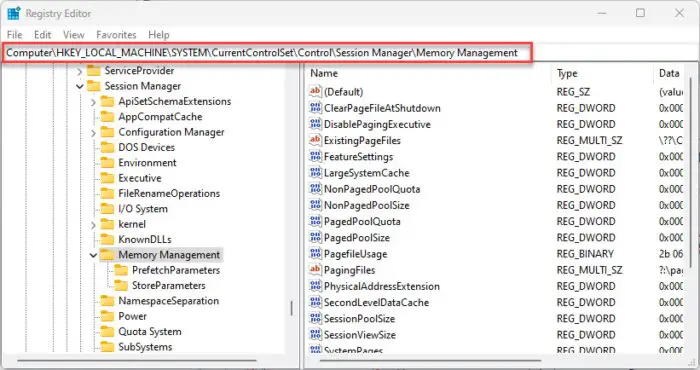
Navigate to the Memory Management key -
Double-click the DWORD “ClearPageFileAtShutdown” and set its Value Data to 1.
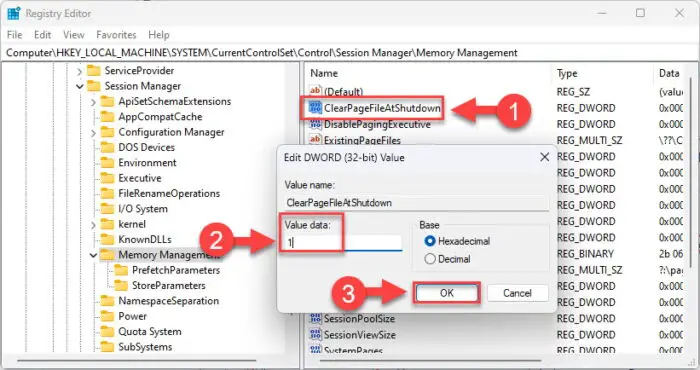
Clear Pagefile at shutdown -
Restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
When the computer restarts, the Pagefile will be cleared. This will happen every time the computer shuts down or restarts.
Update Device Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can often cause memory leaks, which then result in significant memory cache sizes. To fix this issue, make sure to update all system drivers.
Here is a detailed guide to update drivers automatically. If you encounter issues with it, then you can also manually download a driver from the manufacturer’s website and install the driver manually.
Clear Memory Cache using RAMMap
RAMMap is a tiny tool by SysInternals that can be used to clear the memory cache at the press of a few buttons. Use the following steps to use the tool and clear out the RAM cache:
-
Download RAMMap from here.
-
Extract the contents of the downloaded file and run the RAMMap application.
-
Click “Empty” from the ribbon menu of the app, and then click “Empty Standby List.”
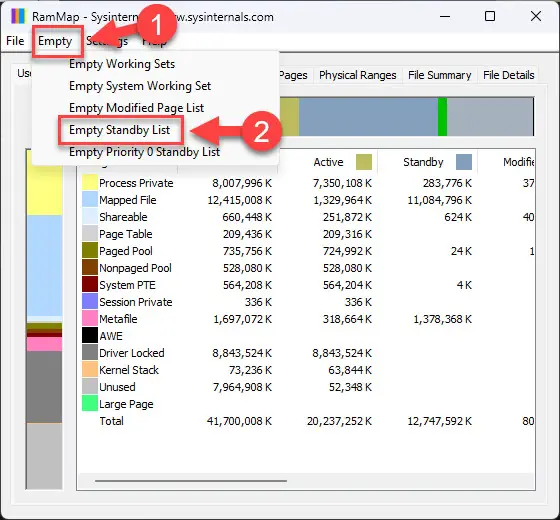
Clear memory cache from RAMMap
That’s it! If you will notice in the Task Manager, the memory cache will be cleared.
Conclusion
Not many people may pay attention to it, but the memory cache is a real thing and can affect your computer’s speed and performance. Ridiculous sizes of memory cache can result in other errors, such as “Out of memory” errors in Chrome or Adobe applications.
Therefore, it is advised to always keep an eye on the size of the memory cache, and clear it out from time to time, especially if your computer has been running for prolonged hours.