Microsoft System Configuration utility (msconfig) is a built-in tool in Windows that helps users control what’s run on the system on startup and troubleshoot your system problems. It can also be used to enable or disable different services, drivers or change Windows boot settings.
In this article, we will explore different ways of using msconfig tool in Windows. Although msconfig has been a part of Windows for quite a long time, it has evolved in recent times and the greatest feature set of msconfig can be found in Windows 8 or Windows 8.1. So we will be concentrating on how we can use msconfig tool effectively in Windows 8 and Windows 8.1.
Opening System Configuration Utility
There are quite a few ways to open msconfig in Windows. Let’s quickly go through some of the ways:
Using File Explorer
The actual msconfig utility is located in System32 folder of Windows. The exact path is:
C:WindowsSystem32msconfig.exe
You can browse through to the utility and open it from there.
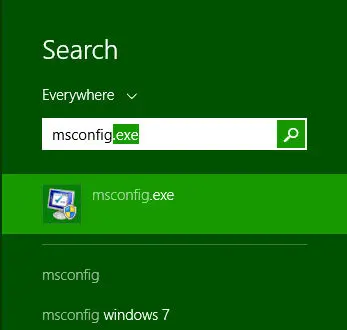
Using Charms Bar
- Press WinKey+C to open Charms bar.
- Go to ‘Search’ and type ‘msconfig’.
You should get msconfig.exe in the search results.
Using Run Command
This method is the easiest and most convenient of all methods.
- Press WinKey+R to open run command.
- Type ‘msconfig’.
This should open the system configuration utility within no time.
Using Command Prompt
- Press WinKey+X to open the menu ->Select Command prompt.
- Type ‘Start Msconfig’ to open the msconfig tool.
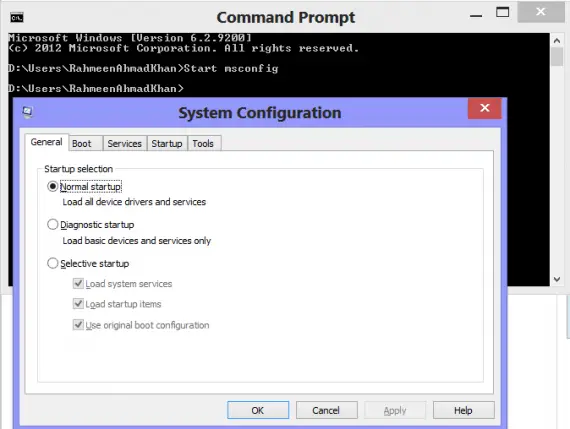
Configure Startup Modes
System configuration utility lets you select a startup mode for your system.
- Check the ‘Normal startup’ box if you want to load all the drivers, services and startup items.
- Click Apply -> Ok
If you are facing any malfunctioning in the Windows and wish to spot the root of problem, start your Windows in the diagnostic mode. In the diagnostic mode, only basic devices and services are loaded to run your system.
If you face the same problem in diagnostic mode too, it means that the basic devices or services are corrupted and you may need to re-install the operating system.
‘Selective Startup’ provides you even more choices among loading boot services, system services or the original boot configuration.
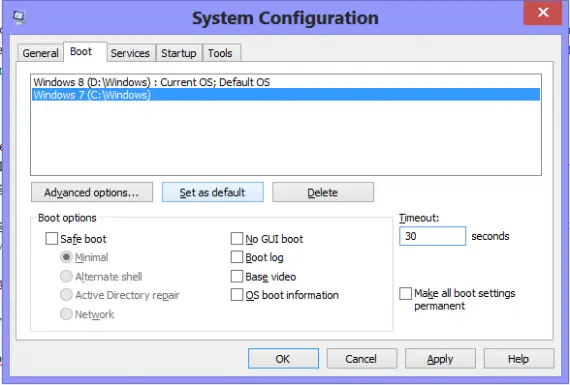
Configure Boot Settings
Sometimes you need to Start Windows in Safe Mode. There are different ways to enter the safe mode and the most easiest one is to use system configuration utility.
Go to MsConfig-> Select ‘Boot’ tab -> Check ‘Safe Boot’ -> Apply -> Ok -> Restart.
We find it important to explain different boot options listed in MSConfig:
Minimal
It is the ‘Standard Safe Mode’ and does not include video card’s driver so your Windows will start in the resolution of 800×600. This option is suitable when you have no idea of the problem and want to load only the minimal services and routines, needed to run your system.
Alternate Shell
This is another name for ‘Safe Mode with Command Prompt’. It opens the command line interface and you can troubleshoot the graphical issues. It does not load the networking drivers and you won’t have internet access in the Alternate Shell Mode.
Active Directory Repair
Active directory contains the machine specific information such as data related to the computer hardware. This mode can help you repair or store new information in the Active Directory to bring back the system stability which may have got disturbed due to installment of any new device/hardware such as motherboard.
Network
‘Safe Mode with Network’ is useful when you are certain that the cause of the problem is not in the Network itself. This mode has a graphical user interface with Internet access and you can download the latest software or drivers from manufacturer’s website to fix the problem of missing drivers or installing the new hardware properly.
You can also change the default Operating System and the ‘Time out’ period using system configuration utility. You can change this time by typing the desired time in the ‘Time out’ box, located next to Boot options. ‘Time out’ is the time your system waits for your choice, before it boots using the default Operating System. To change the default boot settings:
- Go to MsConfig -> Boot tab.
- Select the ‘Windows 8’ (or your choice) from the list of installed operating systems on your PC.
- Click ‘Set as Default’ -> Apply -> Ok
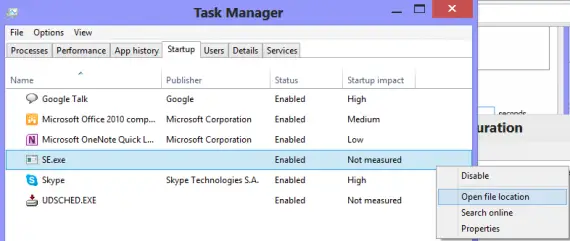
Speed up the system using msconfig utility
Every time you start your system, some programs and services are invoked implicitly. These are startup items and can be enabled or disabled as desired. These items can be managed by a Task Manager where the program name is listed with its publisher, status and start-up impact. Disable unnecessary startup items or items with a ‘high’ impact to increase your PC speed.
- Go to msconfig-> Select ‘Start up’ tab ->Open ‘Task Manager’.
- Select any item -> Click ‘Disable’ button.
- You can also see the properties of any item by right clicking on it.
Services and Tools
The Services tab serves the purpose of enabling or disabling any services that run on the system startup. The Tools tab contains core tools that are important to configure your system settings e.g., computer management, system information, event viewer, change UAC settings etc.
- Go to msconfig –> Select ‘Tools’ tab –> Select any tool –> Click Launch
Please note that every time you change a setting using system configuration utility, you will be asked to restart Windows in order for the changes to take effect. Sometimes it isn’t necessary to restart Windows like when you uncheck a system service to stop loading at Windows startup, you can simply stop that service by going to the Services management console (Run –> services.msc). The service won’t run when you restart your computer next time.
Conclusion
System Configuration Utility (msconfig) provides a wealth of configuration information for Windows. It is up to us how intelligently we use this utility. If you are a real techie and want to test some third party tool to troubleshoot a Windows startup, you may want to use Hijackthis for this purpose.




2 comments
msconfig user
I have a problem with my computer. I have disabled some items in the startup from msconfig but then I deleted them from the registry. But I saw that in msconfig my computer was starting in selective mode. I changed it to normal mode and restarted my system. It was back to selective mode. I have restarted my system several times but the problems remains the same. Is there any solution to this msconfig problem?
Communicator
Good luck Bud, I have studied “MSCONFIG” for years and these days I wouldn’t touch it in a fit and here are my reasons : 1. Windows dynamically configures itself. 2. In a nutshell their are to many Windows settings configured automatically, on this basis not to be tampered with. 3. Many times it draws you in or your told to find and fix the problem in this little box called ”msconfig” well don’t. 4. Every time it has caused more problems than its worth…believe me. 5. THE SOLUTION !!!… your better off refreshing your beloved computer because you’ll end up having to anyway. 6. After your refresh don’t even open that little ‘jack in the box’ called yours truly “”mssssssconfig””. 7. Enjoy your new refreshed little Master Communicator. Good Bye and may the new force be with you !.