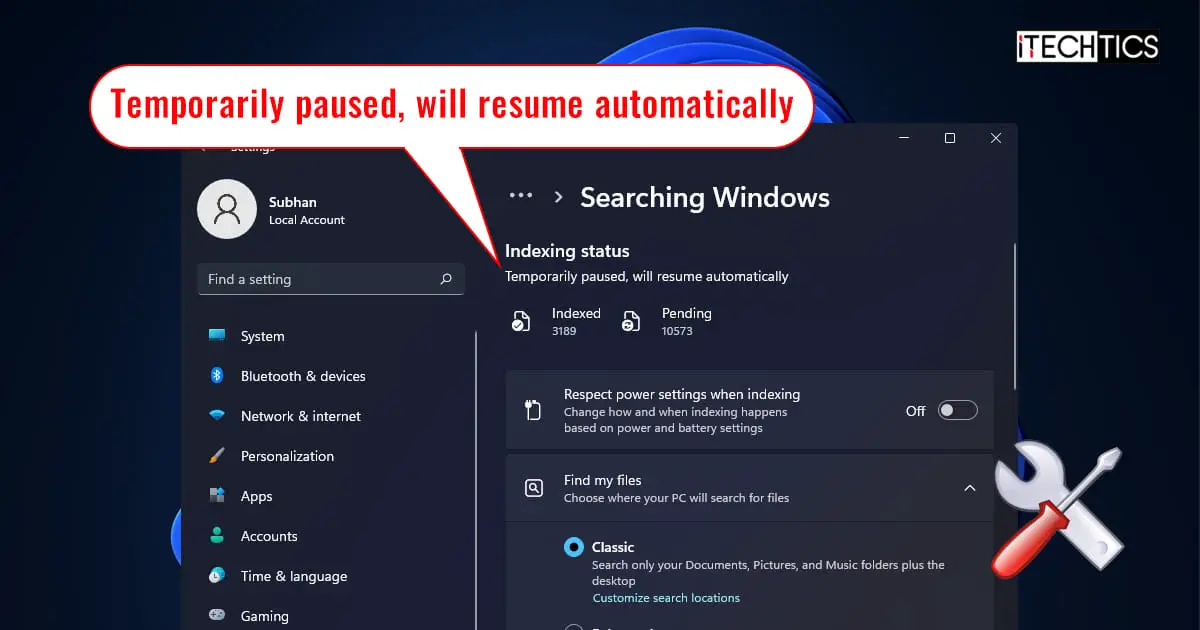
While performing a search for a file, folder, or email using the Search Box or the Start Menu in Windows 11, you may have trouble getting back the desired search results, or it could take minutes for the results to even show up. Often, people know that an application is installed on their computer, but it does not show up when searching for it.
When you go to the respective Settings page, you will see that the indexing status is “Temporarily Paused.” This can be one of the reasons why you won’t see your desired data while searching for something.
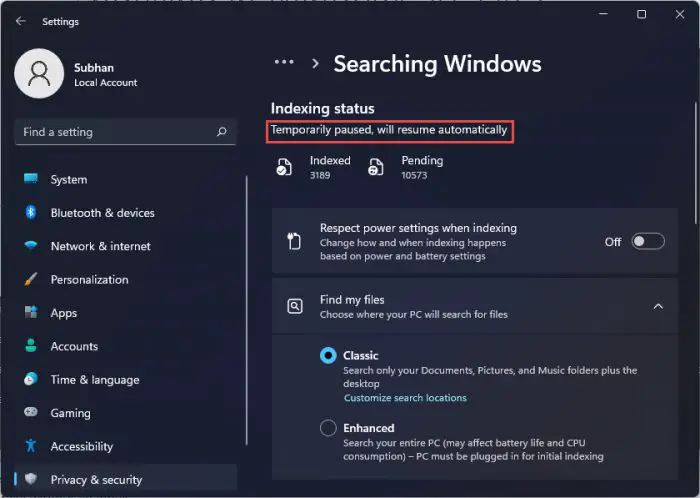
This post discusses what Indexing is, how it works, how you can get it back up and running again, and how you can optimize it to get quicker, more accurate search results.
Table of contents
What is Indexing?
In Windows, indexing is the process of storing file data, such as its content, metadata, dates associated, etc., so that the operating system can perform a “lookup” when the user performs a search.
When you perform a search in the Search Box, via Cortana, or in the Start Menu, Windows fetches similar results from the cataloged (indexed) data and shows it to you. If some data has not been indexed, it will not turn up in the search results.
Indexing is running on your computer all the time, unless stopped/paused manually. This is because continuous changes are being made to files and folders that need to be cataloged. The first time you install Windows, it takes a while for the PC to index the initial data. After that, only the changes made to the data are indexed.
By default, Windows 11 indexes the data from the following locations:
- Internet Explorer history
- Microsoft Outlook (if installed)
- Start Menu items
- C:\Users (excluding AppData folder)
You can add more locations to be indexed, or remove them from the given list. You can also have your entire PC indexed, but it has its repercussions. The method to modify the indexing locations has been discussed further down this post.
Microsoft’s rule is that the indexed information should not be any higher than 10 percent of the total indexed files. For example, if the indexed files are 100 MB, the index for those files will be less than or equal to 10MB.
Indexed data is stored locally on your computer and is not communicated to Microsoft or any other location. However, it may still be possible for an application to read and/or share that data without you knowing.
What Causes Indexing to Pause?
As you may already know by now, indexing is important for you to get to a file/folder quicker by searching for it. However, if you find that it is “paused,” it can be due to several reasons:
- Indexing could be manually paused.
- Indexing has automatically paused due to misconfigured settings.
- Corrupted or missing system files could cause indexing to not perform properly.
- Windows Search, a service responsible for indexing and fetching search results, could be disabled or malfunctioned.
- The indexing library, containing the indexed catalog, could be corrupted.
- Corrupted Windows Registry Transaction files found in the “TxR” folder prevent Windows Indexing from functioning properly.
Let us now show you how to fix the issue and get your Windows Search back up running normally again.
Fix File Search and Indexing Not Working in Windows
Run Search and Indexing Troubleshooter
Windows comes with a built-in troubleshooter for certain Windows components, which are convenient to use and usually fix the problem. Microsoft gives a dedicated troubleshooter for Windows search that you can use to fix the issue. Here is what to do:
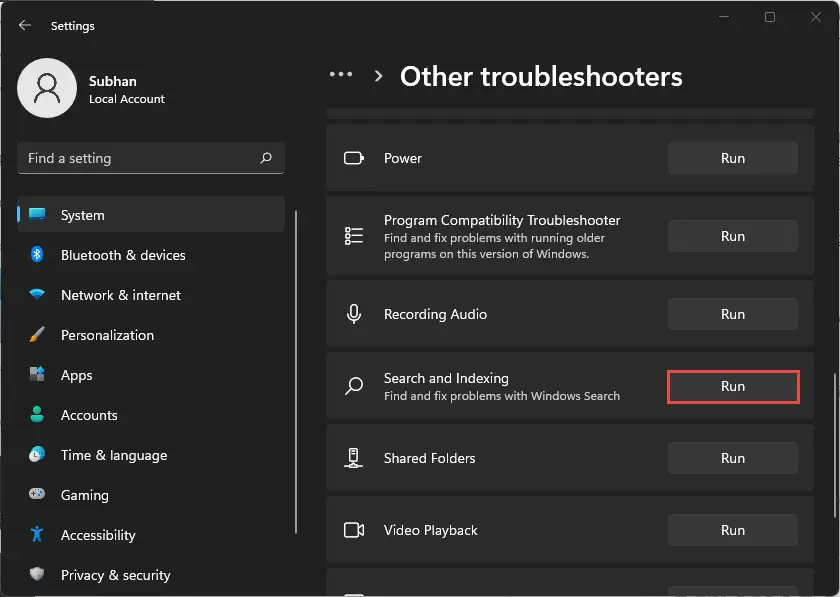
- Navigate to the following:
Settings app >> System >> Troubleshoot >> Other troubleshooters - Here, click Run in front of “Search and Indexing.”
- The troubleshooter wizard will now open. On the first screen, check the box(es) for the symptoms you are witnessing. When selected, click Next.
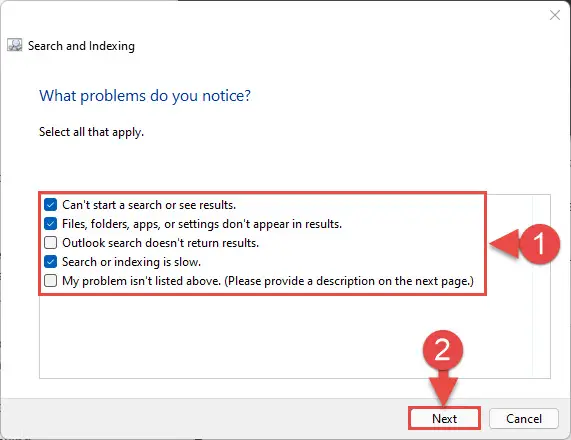
- Next, you will be asked for a brief description of the issue. Enter the symptoms you are experiencing (optional) and click Next.
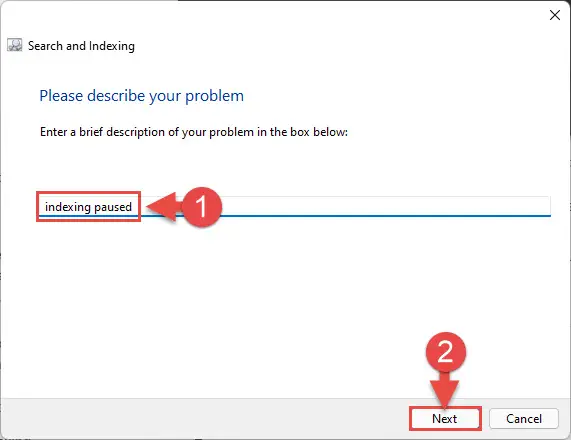
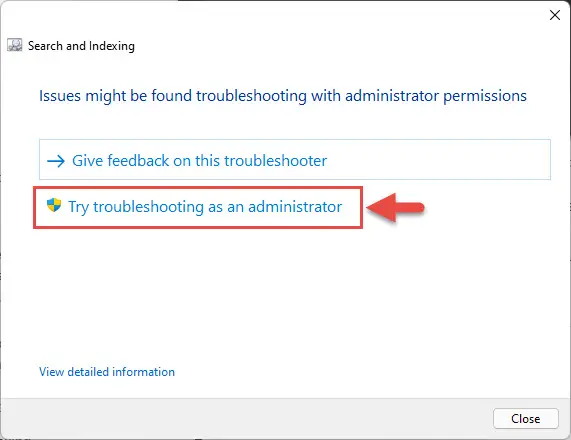
- Now click “Try troubleshooting as an administrator.”
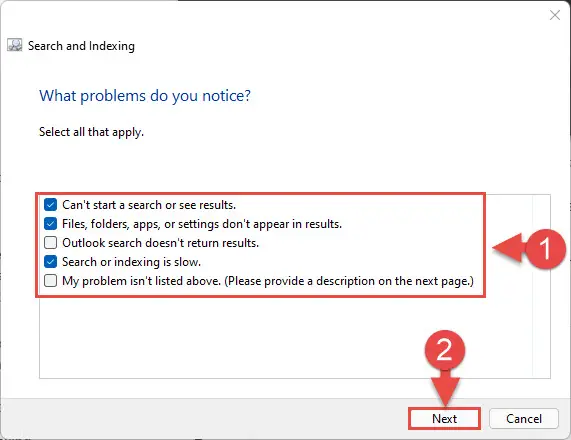
- Now check each box next to the symptoms you are experiencing again, and then click Next.
- The troubleshooter will now perform a search and may recommend a solution. If it does, click Apply this fix.
- Once the fix is applied, close the troubleshooter and check if the indexing has resumed again.
Disable Search Indexing from Respecting Power Settings
Since indexing is always running in the background, Windows provides a setting to disable it when you are running low on battery, in the case of a laptop. It may be possible that indexing has paused due to this reason. If so, you can change indexing settings and allow it to disregard the power settings and re-enable indexing.
- Navigate to the following:
Settings app >> Privacy & security >> Searching Windows - Here, toggle the slider in front of “Respect power settings when indexing” into the Off position.
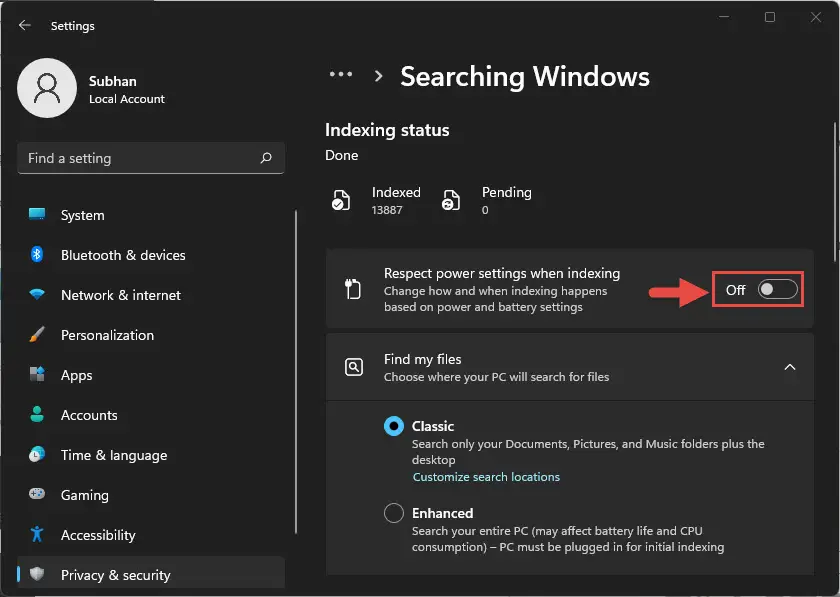
Now check to see if indexing has resumed again.
Start Windows Search Service
As discussed, as the service responsible for running indexing may have been disabled, causing indexing to not function properly. If so, it needs to be re-enabled. Here is how:
- Open the Services Console by typing in services.msc in Run.
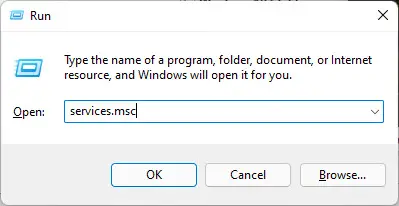
- Here, right-click “Windows Search” service and then click Properties from the context menu.
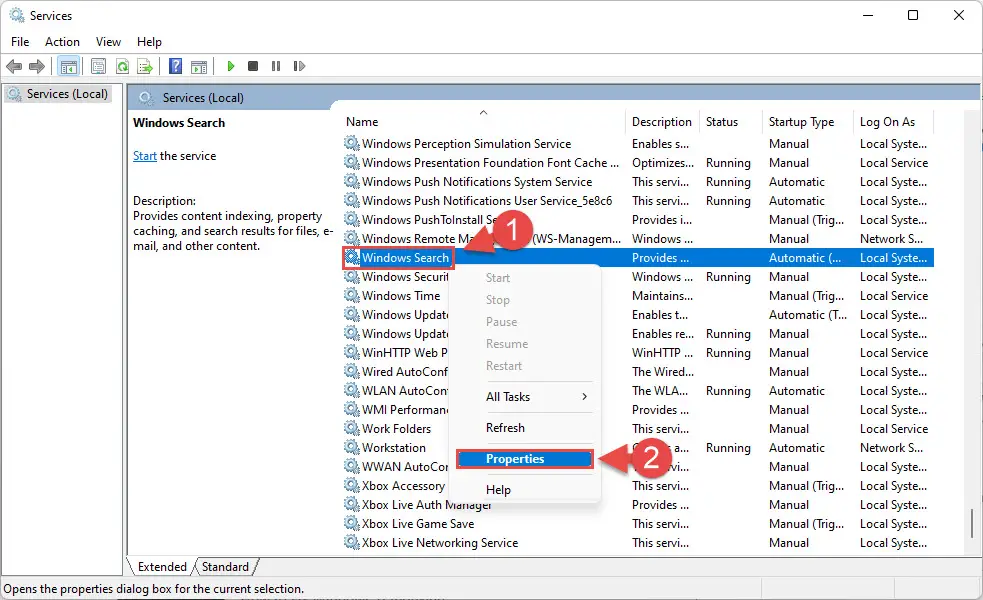
- From the Properties window, select “Startup Type” as Automatic (Delayed Start). Then, click Start to start the service. When it does, click Apply and Ok.
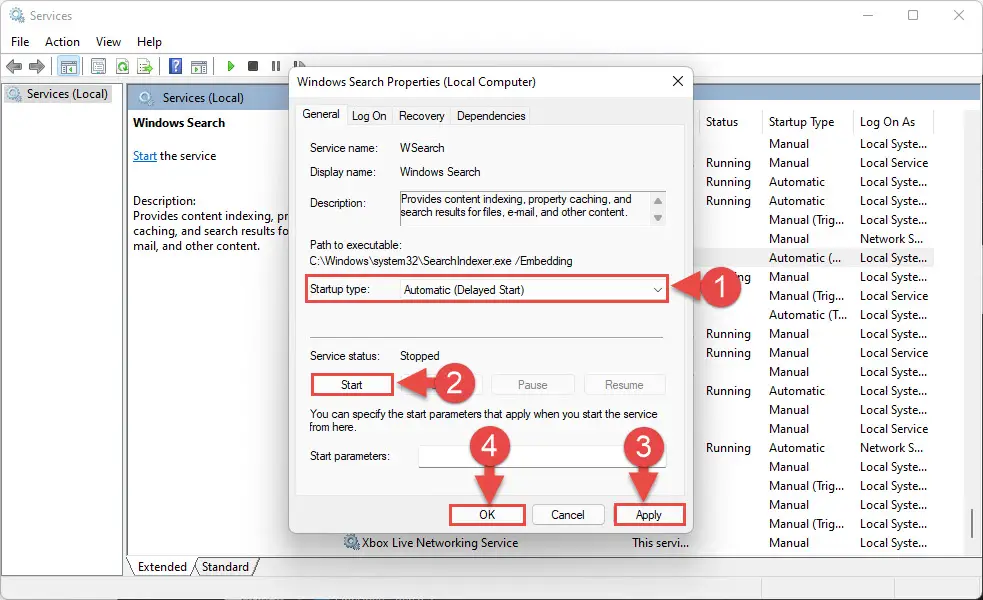
Note: If you see the service already running, right click on it and then click Stop. When it does stop, right-click it again and click Start to restart the service.
Now check if the problem has been resolved.
Rebuild Indexing Library
The problem with the indexed library could cause the feature to not function properly. In that case, the entire cataloged data needs to be rebuilt from scratch, which can take a while, in some cases, hours. That said, it could potentially fix the issue for you. However, you may not be able to perform any searches during the rebuilding process.
Perform the following steps to rebuild the indexing library:
- Navigate to the following:
Settings app >> Privacy & security >> Searching Windows >> Advanced indexing options - The Indexing Options window will now open. Here, click Advanced.
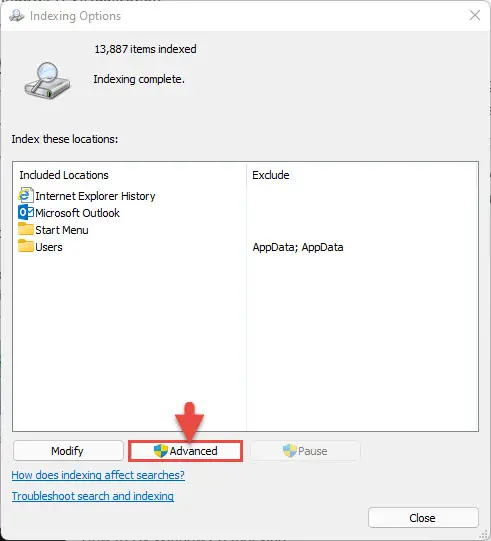
- From the Advanced Options popup window, in the “Index Settings” tab, click Rebuild under Troubleshooting.
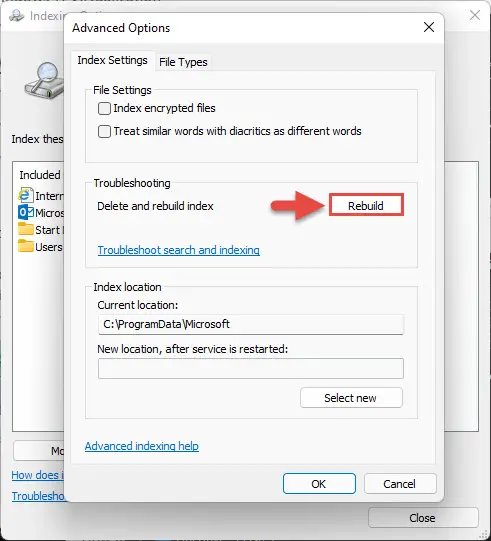
- On the confirmation dialog, click OK.
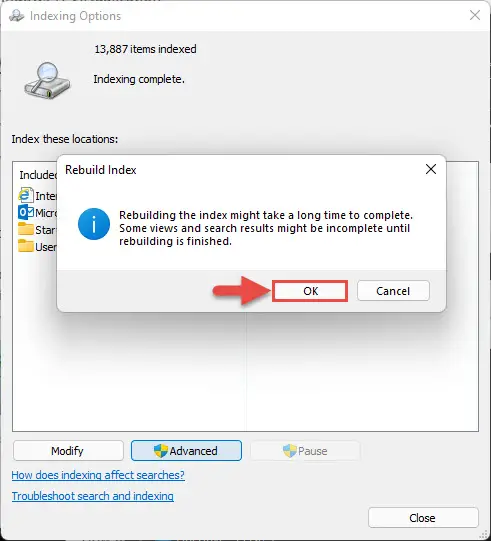
The indexing process will now commence. At this moment, you may notice that significant system resources are being consumed, which is normal.
Please note that the above mentioned configurations will only open if you are logged in as an administrator.
Once the process is complete, check if the indexing process is still paused or not.
Fix Missing Windows Registry Entries
This issue may be caused by missing or corrupt Windows Registries. These can be fixed/restored by deleting the files that log the transactional changes in the Registry.
File with extensions.BLF and .REGTRANS-MS stores this information, which can be located in the “TxR” folder. To fix the issue, these files need to be deleted, and Windows will recreate them upon the next reboot.
Here is how to delete the files:
Note: The following steps must be performed from an administrative account.
- Open Windows Explorer, click on the ellipses (3 dots) on the ribbon menu and click Options:
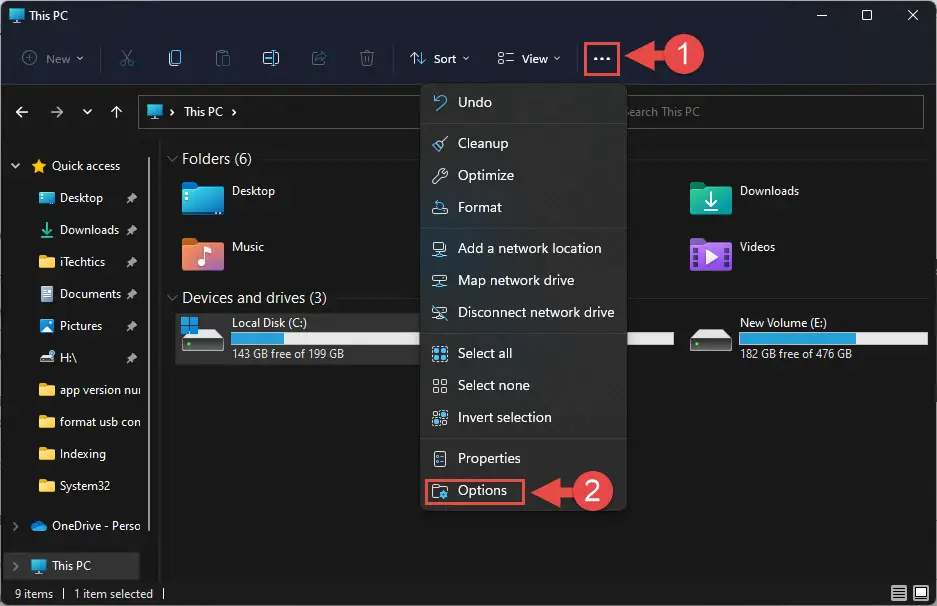
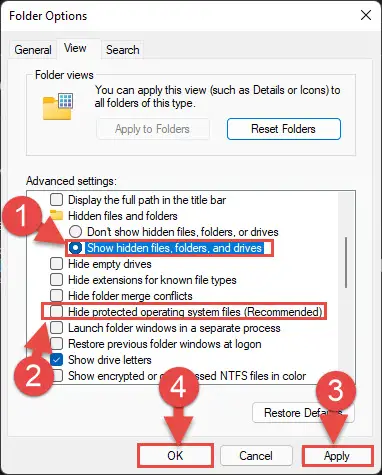
- From the Folder Options window in the View tab, select the “Show hidden files, folders, and drives” radio button. Then, uncheck the box next to “Hide protected operating system files (Recommended).” Now click Apply and Ok:
- Now use Windows Explorer to navigate to the following location:
C:\Windows\System32\config\TxR - Here, select all “BLF” and “REGTRANS-MS” files and delete them.
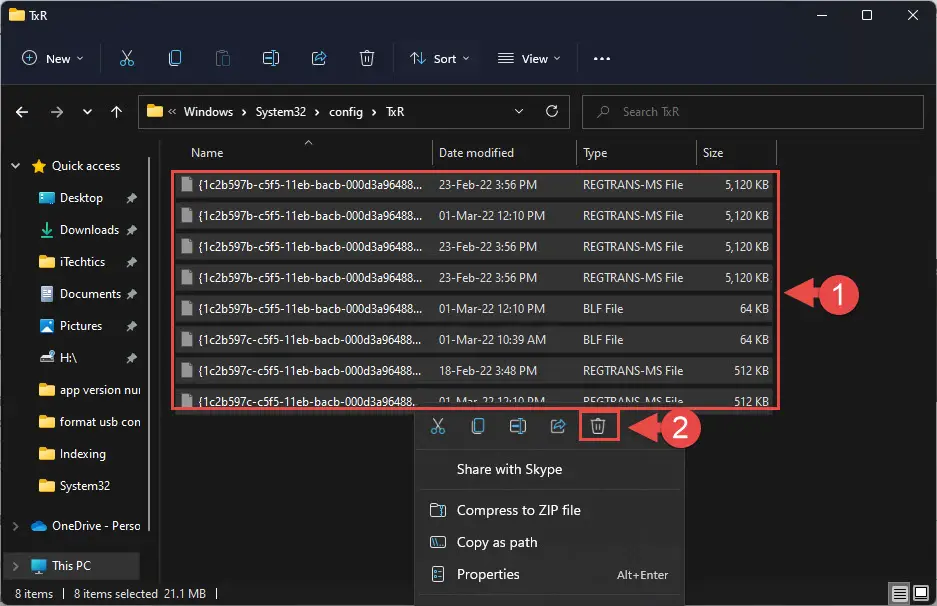
- Once all are deleted, reboot the computer.
As the computer reboots, you should observe that indexing has now resumed.
If you are still unable to resolve the issue, try one last trick that you can perform to fix it.
Run DISM and SFC Repair Tools
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) and System File Checker (SFC) are command-line tools in Windows that allow you to perform repair tasks.
SFC performs a deep scan of your Windows system files and searches for missing or corrupted content. If it finds any anomalies, it replaces these files with redundant files on your PC that may be available at another location.
DISM can be used to prepare, modify, and repair system images. However, you need an active internet connection to download and replace corrupted content from Windows Update.
You can use both of these tools using our guide here.
We certainly hope that the solutions discussed in this post have resolved your problem. If they have, continue reading to learn how to manage the different indexing settings.
How to Perform Search Through Entire PC
We had mentioned that Windows only indexes a few locations by default. However, you can expand this search through your entire computer in a few clicks. Here is how:
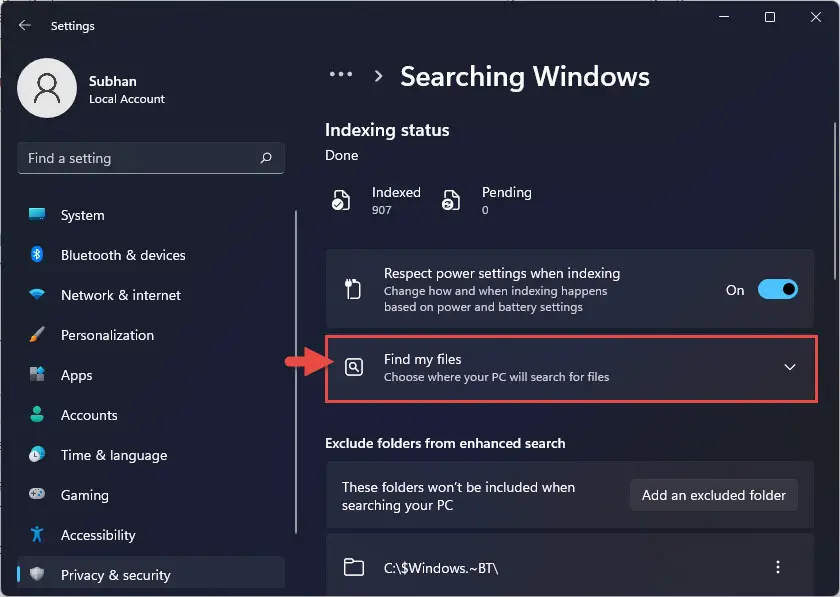
- Navigate to the following:
Settings app >> Privacy & security >> Searching Windows - Here, click on Find my files to expand the menu.
- From the expanded menu, select the Enhanced radio button.
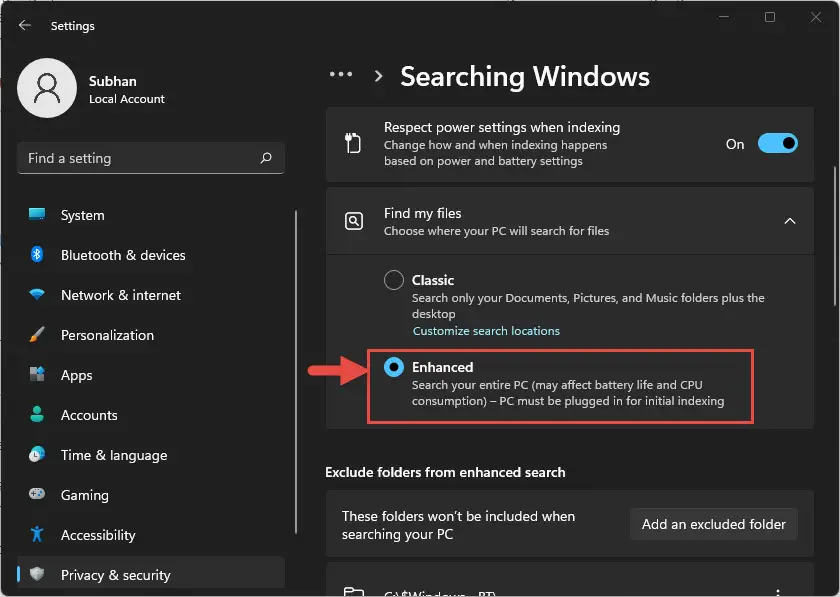
When you perform a search, any relevant content found across your PC will be shown in the search results, as everything is now indexed.
How to Add or Remove Indexing Locations
As we had mentioned at the start of this post, you can add or remove locations within your PC to be indexed. Reducing the indexing location will fetch the results faster, increasing your productivity. However, simultaneously, you may not be able to see all the results from various locations on your computer.
If you increase the indexing locations, you may be covering more ground, but it will take just as long for Windows to grab the relevant results from all locations.
Here is how to modify the indexed locations on your computer:
- Navigate to the following:
Settings app >> Privacy & security >> Searching Windows >> Advanced indexing options - From the Indexing Options window, click Modify.
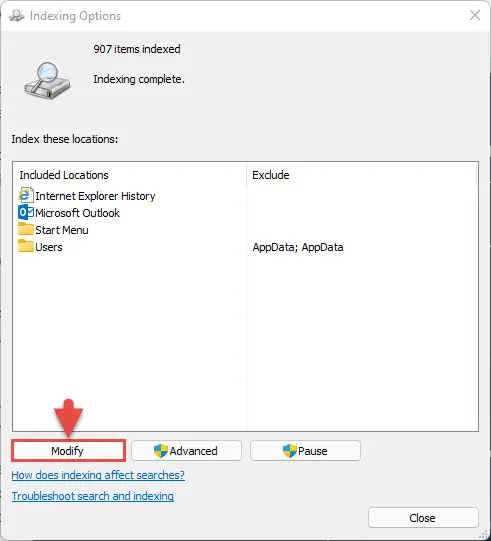
- From the Indexed Locations window, click Show all locations from the bottom.
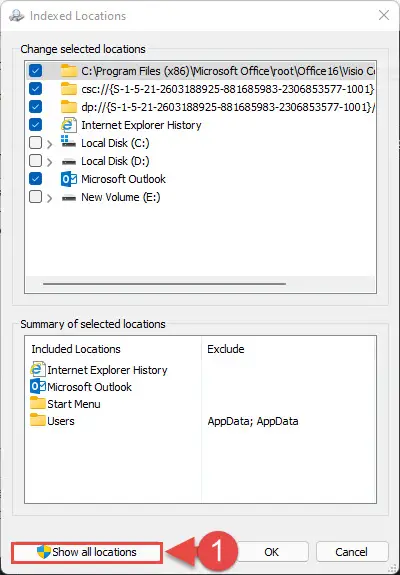
- Now check the boxes next to the location you want to index and uncheck the boxes next to the locations that you do not want indexed. Once you are done, click OK.
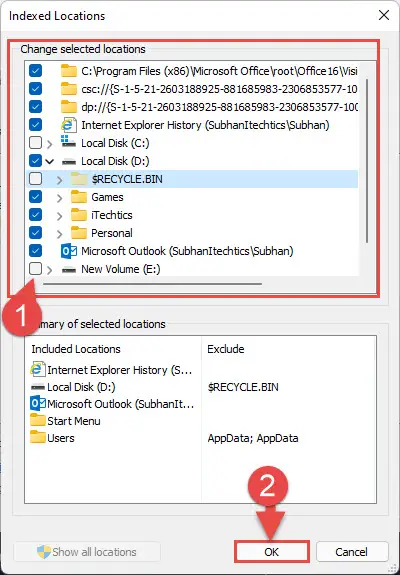
Windows will now begin indexing the new locations added (if any).
How to Add or Remove Indexed File Types
You can not only manage the indexing locations, but also the file types that are indexed. You can even add a custom file type to be indexed if it is not available in one of the given options.
Perform the following steps to add or remove indexing file types in Windows 11:
- Navigate to the following:
Settings app >> Privacy & security >> Searching Windows >> Advanced indexing options - From the Indexing Options window, click Advanced.

- From the Advanced Options window, switch to the File Types tab. Here, uncheck all the boxes next to the file types that you do not want indexed, and leave the boxes check to which you do want to keep indexing.
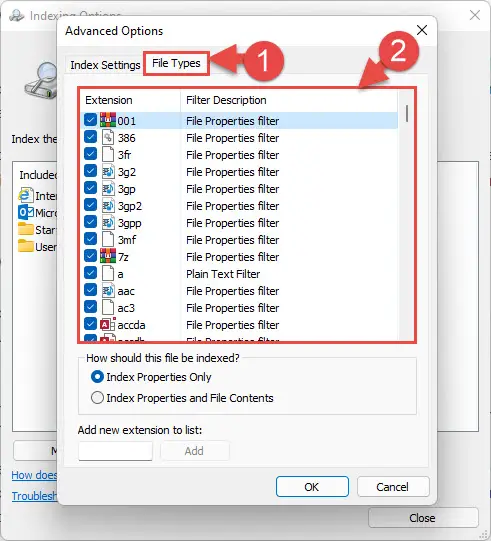
- You can also index the Properties of these files, or index the Properties as well as their content. Furthermore, you can also add a new file type to the index from the text field at the end of the Advanced Options window. When done with the configurations, click Ok.
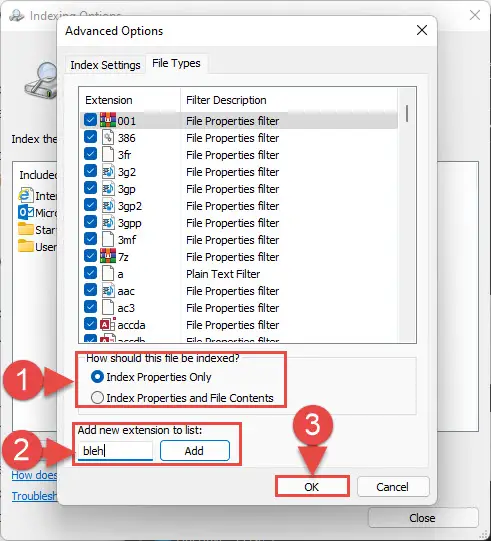
Windows will now begin indexing new file types (if any).
Closing Words
Most Windows users usually do not optimize their search results, as long as they can access the right files and folders using the indexed data. However, optimizing the indexed locations and file types significantly improves the time Windows takes to fetch the results, thus increasing your productivity.
When indexing is paused, new data is not being cataloged, causing a nuisance. You can fix the issue using the given methods in this post and get your operating system to behave as it should, without having to repair or redo our OS.