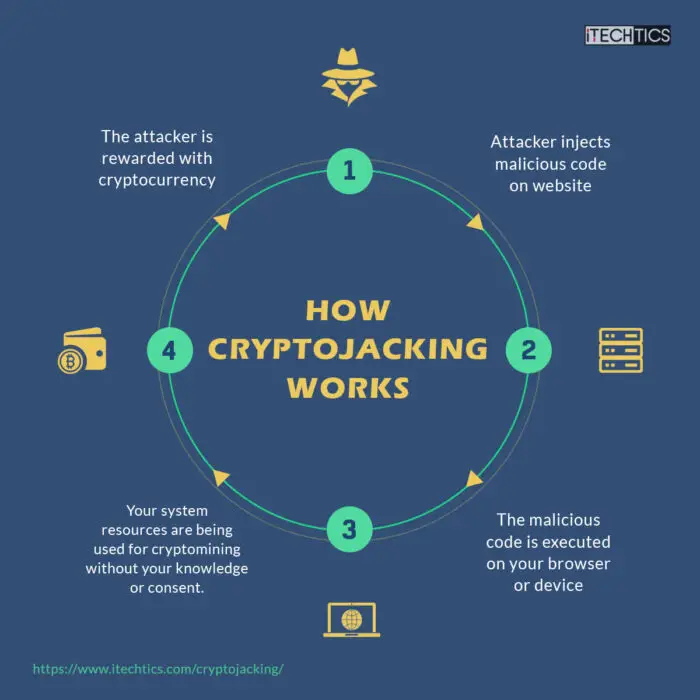
Cryptjacking is a kind of malware attack where the attacker uses the system resources of other people to mine for cryptocurrencies without their authorization. Although it does not inflict any direct harm, it can incur costs to businesses and organizations in terms of power consumption, adding additional hardware to boost system performance, and human resource costs for troubleshooting performance issues.
If you are into mining cryptocurrencies or trading in them, then you may already be familiar with cryptojacking and its techniques. But if you are not aware of what it is and how it works, then you may want to hang tight and learn how to protect your devices from cryptojacking, since it can happen to anyone.
This page covers
What are cryptocurrencies and cryptomining
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies whose records are maintained by decentralized systems. These are alternative forms of payment that people can use to trade with. Like different real-world currencies with different worths, there are over 3000 forms of cryptocurrencies with different worths, like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Some people trade real-world money, like dollars, to purchase a certain amount of cryptocurrency, while others trade computing power in return for digital money.
Cryptocurrencies work on the concept of blockchain, which is a chain of blocks scattered across the globe. These blockchain tables are regularly updated to keep track of all the accounts and the trading that is happening. This amount to be a lot of calculations results in a lot of computing power. For this, cryptocurrency owners rely on third-party system resources, like regular end users, to fulfill the computing power.
Users “mine” cryptocurrencies by providing their system resources to the blockchain system so that they can maintain the records, and in exchange, they would be rewarded with cryptocurrency. This has actually resulted in businesses being established that provide raw computing power from high-spec GPUs, which also incur all the electricity costs, and in return, they make digital money.
This is how money is made in the cryptocurrency world, and understanding this concept is crucial to understanding how cryptojacking works, where the attacker makes money using your system resources without you knowing about it.
What is Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is when an attacker uses system resources without the owner’s knowledge to mine cryptocurrencies. This malicious act of intrusion and injecting code without authorization is a cybercrime, even though it does not directly harm the user’s data or their privacy.
Cryptojacking can use any device that has computing power, which includes computers, mobile phones, tablets, etc. The device is injected with malicious code which is executed in the background and begins the mining processes. Cryptomining then uses system resources (extensively) to maintain and update the blockchain tables.
The malicious piece of code or process is normally disguised to hide amongst other legitimate items. This is so that it can run without being detected, and the attackers can financially benefit in digital currencies. The purpose of cryptojacking is to use other people’s hardware resources and electricity costs and generate revenue for themselves.
Note that there are also other methods of performing cryptojacking. For example, certain cryptojacking JavaScript webpages execute mining processes while the users are on the website. This practice is still being used by legitimate website owners who are transparent about what they are doing while the user is still on the website. Such cryptojacking activities usually come to a halt as soon as the user leaves the website.
How cryptojacking works
The first step in cryptojacking is to plant the malicious code onto the end user’s devices. This can be done in one of two ways:
- By sending phishing emails and getting them to click on malicious links, which downloads the malicious code.
- Injecting the malicious code on websites (normally without the owner’s knowledge) or an online ad using JavaScript which automatically executes in the victim’s browser.
Normally, both of these methods are adopted by attackers to maximize their revenue streams. The victim then normally uses their device while the malware installs the cryptojacking script into the device and lets it run in the background. Regardless of the technique, the script performs complex mathematical operations on the victims’ device and transmits the results to a server under the hacker’s control.
Normally, cryptojacking scripts do not inflict harm on the user’s device. This means that they do not steal information, encrypt the data, or anything else. However, they do steal the computer’s computational power, which results in other processes getting pushed to the back of the queue, degraded system performance, computer freezing, etc.
Effects of Cryptojacking
As previously mentioned, cryptojacking might result in slower system performance, stuttering and hanging, and other performance-related issues. However, it will not inflict direct harm. However, it can incur certain costs.
For one, since your device will consume more power, it will incur electricity costs to the victim. Additionally, your hardware will wear out early as it will be performing more than usual for hours without you knowing about it. This will also incur costs.
In the case of organizations falling victim to cryptojacking, their systems could be hijacked to perform cryptocurrency mining instead of the actual tasks they were meant to do. Moreover, it could also result in the costs of human resources being used to detect and fix performance-related issues.
Detecting Cryptojacking
There is no sure way to tell when your device falls victim to cryptojacking. There are no processes to look out for. Instead, you must look out for the following symptoms:
- Reduced performance: Since cryptomining consumes a lot of system resources, especially the GPU and the CPU, you may experience decreased system performance. Look out for system freezes, crashes, and sluggish performance.
- Overheating: Since more system resources will be used, the components may be overperforming resulting in excessive heat dissipation. You may also observe that the system fans are now running faster for no apparent reason with a lot of noise.
- Excessive resource utilization: If you look into the Task Manager on Windows OS, you may notice that your system resources, especially the GPU and the CPU are being excessively used. If so, and you yourself are not performing any resource-intensive tasks, then it is likely that your device is mining cryptocurrencies.
How to prevent cryptojacking
If you do find yourself in a situation where you suspect that your device is compromised and being used for cryptojacking, there are a few mitigation and prevention methods that you can adopt.
Whether you work alone or within an organization, you and all your colleagues should be educated about the different phishing tactics. Attackers often use phishing emails to bait you into clicking malicious links and buttons for you to unknowingly download the code that will mine cryptocurrency in the background.
Therefore, do not open or click emails that may seem fishy and malicious, and report them to the appropriate authority to prevent others in your organization from falling victim to such scams too.
Perform security scans
You must perform deep scans of your devices to detect any malicious files or patterns, especially if you detect sluggish system performance or overused system resources.
Most reputed antimalware automatically detects malicious code as soon as they land on the PC, or are executed, and immediately quarantined. However, in some cases, a certain type of malware may go undetected, like fileless malware. In this case, a deep scan of the system can help root it out.
You can schedule a deep scan using your trusted antimalware software. If you do not have one, you can use the integrated Windows Security to perform a scan. Here is how:
-
Press the Windows Key + i to open Windows settings.
-
Go to the following:
Privacy & security >> Windows Security >> Virus & threat protection
-
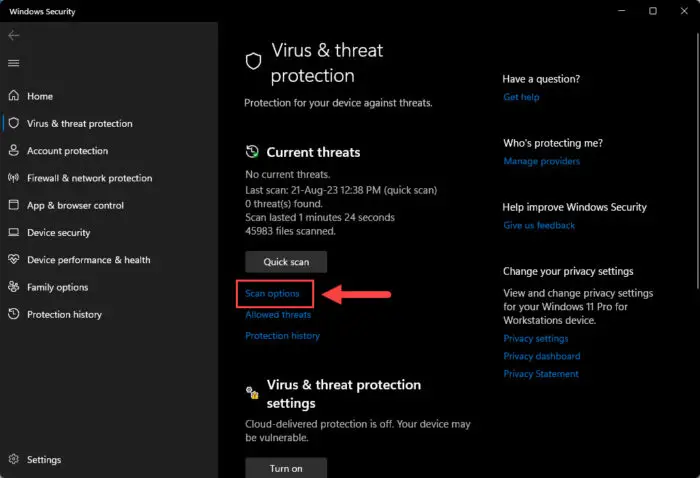
Click “Scan options.”
View Windows Security scan options -
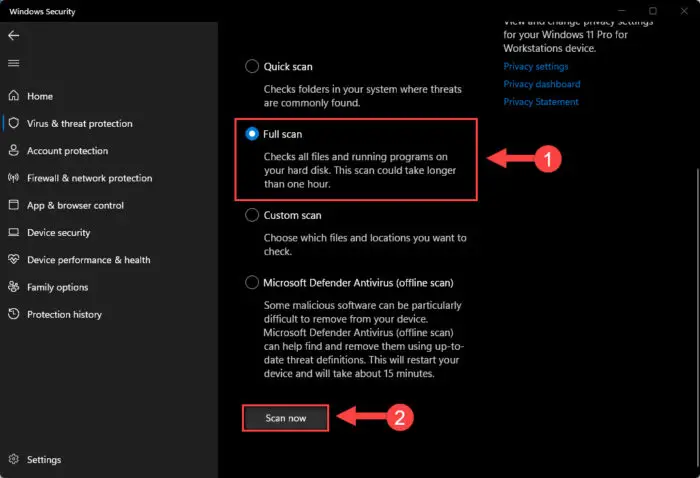
Select “Full scan” and then click “Scan now.”
Perform a full scan with Windows Security
On other operating systems, you can use their provided security software or use a reputed third-party antimalware software.
Use adblockers and anti-cryptomining extensions
Adblockers come as browser extensions as well as dedicated software that you can install on your device. The purpose of adblockers is to eliminate any annoying popups and banners that display ads, which could potentially download malicious code for cryptojacking.
When the adblocker removes the ads, there are fewer chances for you to click on one.
You can find both free and paid adblockers for your specific browser on the internet. As a reminder, always use trusted and reputed software.
Additionally, you can also find web browser extensions that will block cryptojacking scripts from being executed on your browser. Here are some extensions that you can use for this purpose:
Disable JavaScript
JavaScript is a programming language used on websites for dynamically updating content. JavaScript is executed within the web browser which can potentially also include code for mining cryptocurrencies. This is normally what attackers inject into unmaintained and vulnerable websites so that the visitors who come across the websites fall victim to the attack.
Most modern browsers allow you to manage your JavaScript settings. Here are the steps to disable websites from loading JavaScript across different web browsers.
Disable JavaScript on Google Chrome
-
Click on the 3 dots in the top-right corner of the Chrome browser and then click Settings.

Open Chrome settings -
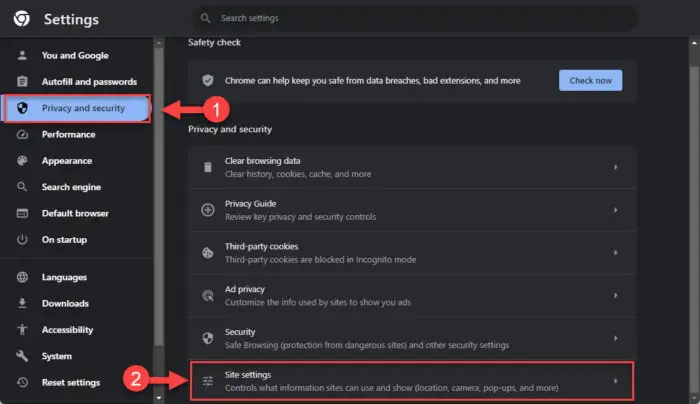
Click “Privacy and security” in the left navigation pane and then click “Site settings.”
Open Site Settings in Chrome -
Click JavaScript in the Content section.
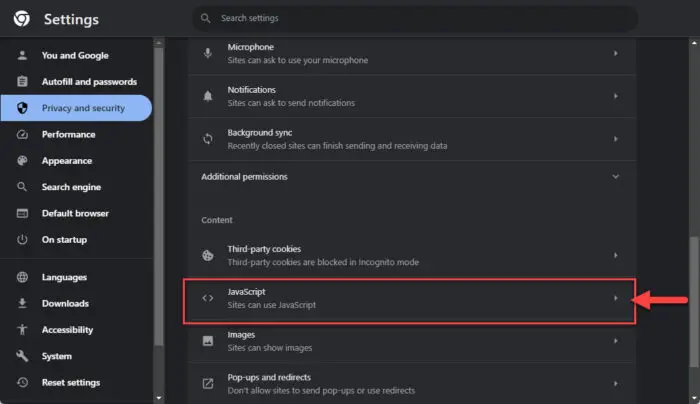
Open JavaScript settings in Chrome -
Select “Don’t allow sites to use JavaScript.”
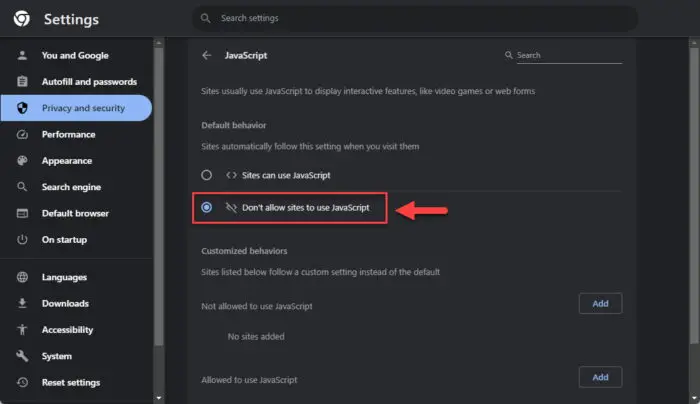
Disable JavaScript in Chrome
Disable JavaScript on Microsoft Edge
-
Click on the 3 dots in the top-right corner of the Chrome browser and then click Settings.
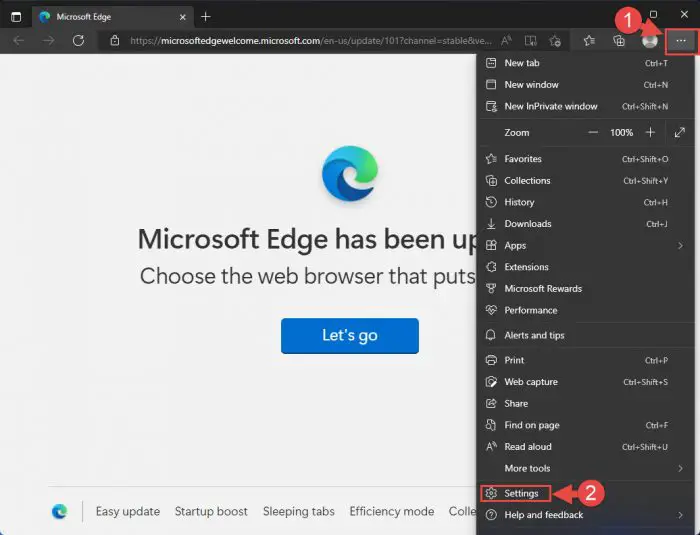
Open Edge settings -
Click “Cookies and site permissions” from the navigation pane on the left, and then click JavaScript.
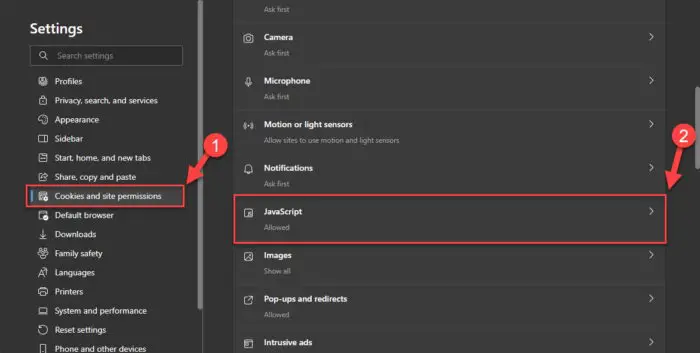
Open JavaScript settings in Edge -
Toggle the slider in front of “Allowed (recommended)” into the Off position.
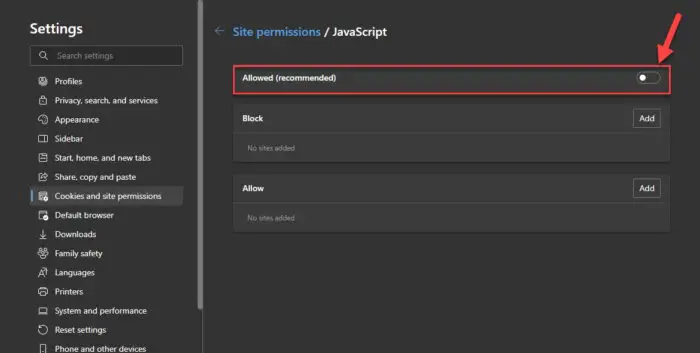
Disable JavaScript in Edge
Disable JavaScript on Opera
-
In the Opera browser, click on the Gear icon in the bottom-left corner to open the browser’s settings.
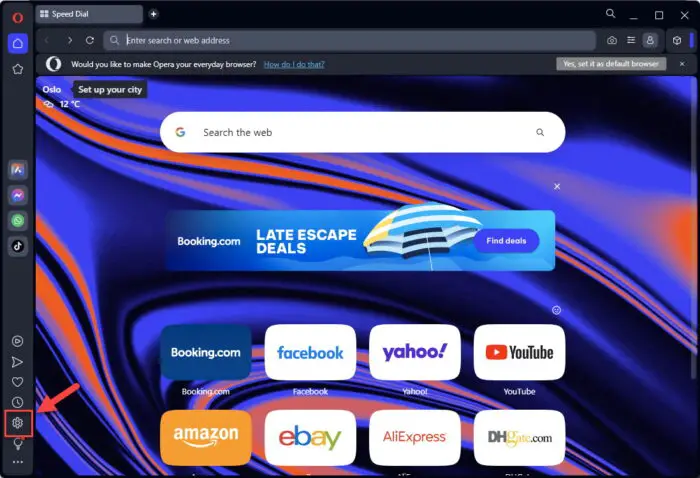
Open Opera browser settings -
Click “Privacy and security” on the left, and then click “Site settings.”
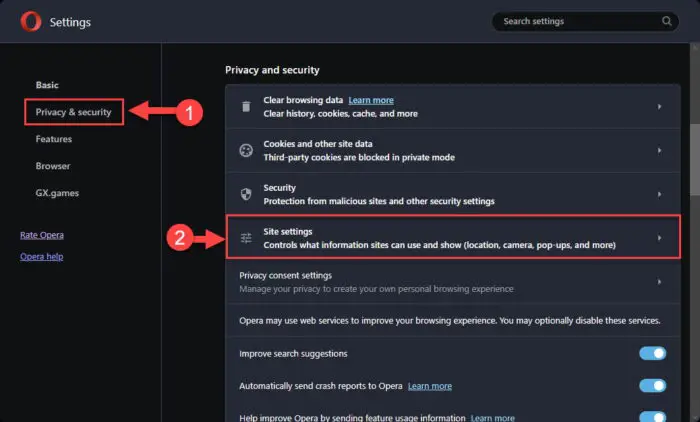
Open Site Settings in Opera -
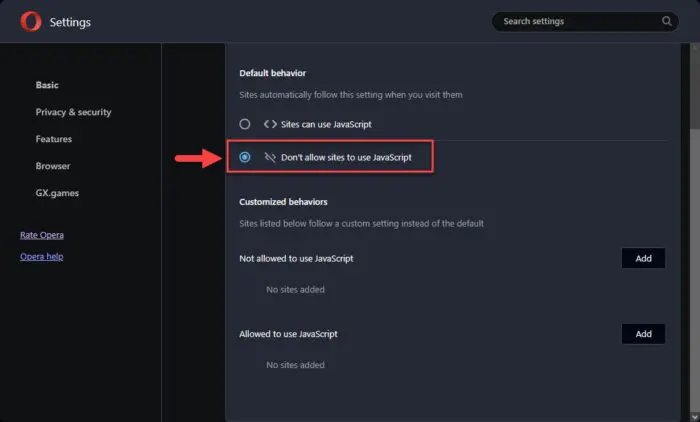
Click JavaScript in the Content section.
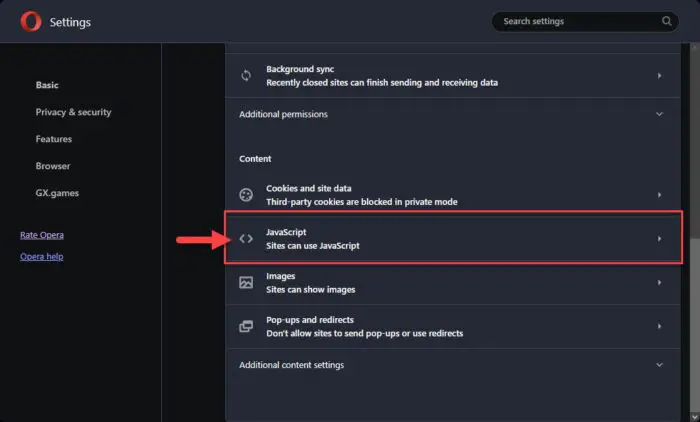
Open JavaScript settings in Opera -
Select “Don’t allow sites to use JavaScript.”
Disable JavaScript in Opera
Disable JavaScript on Brave
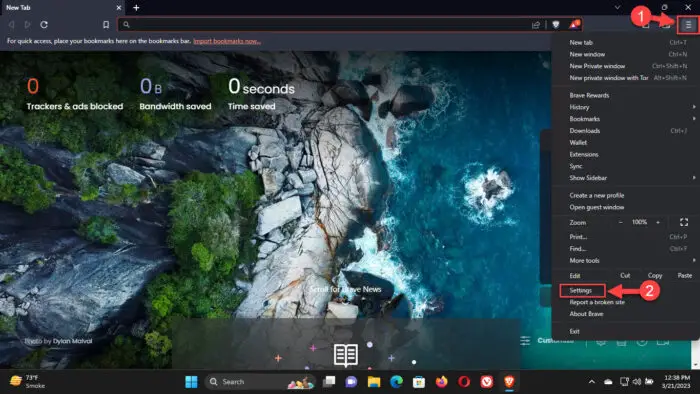
-
Click on the 3 lines in the top-right corner and then click Settings.
Open Brave settings -
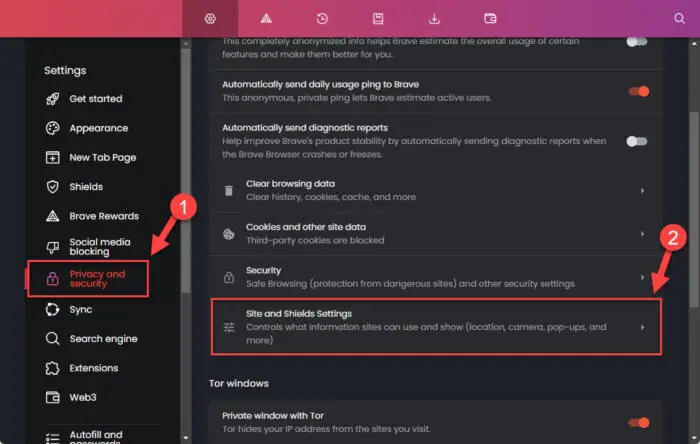
Click “Privacy and security” in the left navigation pane and then click “Site and Sheilds Settings.”
Open Site Settings in Brave browser -
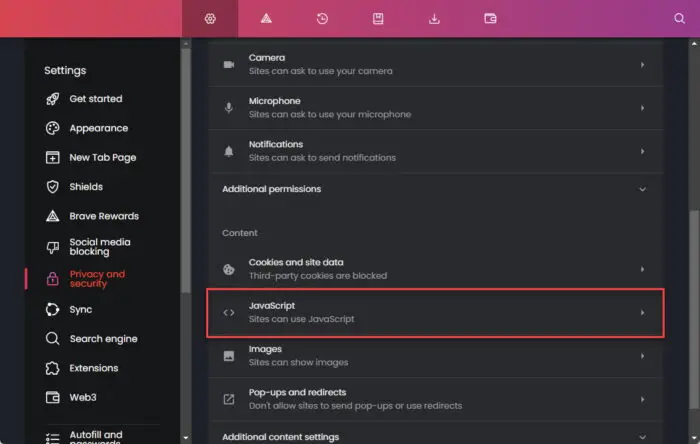
Click JavaScript in the Content section.
Open JavaScript settings in Brave -
Select “Don’t allow sites to use JavaScript.”
Disable JavaScript in Brave
Block known cryptojacking websites
Other than the prevention techniques already discussed, you can also preemptively block malicious websites that are known to deliver cryptojacking scripts to end users. You can find information on such websites all across the internet where they have become notorious after carrying out similar attacks.
Monitor system resources
Although it is not a prevention method, you can monitor your system resource in case it has fallen victim to one of the cryptomining scripts.
In case an attacker does carry out cryptojacking on your device, it would be better to practice the mitigation methods and eliminate it from your PC at the earliest. For that purpose, monitoring your resource utilization through the Task Manager (or other software) is crucial.
Takeaway
We learned that cryptojacking may not be as frightful as the rest of the cyberattacks, it does however cost you something, and not only money. If a reputable organization’s servers are being used for cryptomining and this news becomes public, the company could lose a significant amount in terms of shares and stocks. Not only that, but they would also bear the additional costs of electricity, resource-wearing, and in-place security teams and resources.
Hence, cryptojacking may not be as innocent as you may think. Therefore, we suggest that you take the necessary precautionary steps and prevent your devices from falling prey to suck malicious activities.