Whether you use a modern computer or a smartphone, your device likely has a processor with multiple cores. The processor is the brain of the device which performs the tasks instructed by the various software.
With evolving technology, tiny processors are becoming smaller in size and better in terms of performance. Not only that, but they now include more and more processing cores.
The most modern processors now have up to 24 physical cores (that are publically available), whereas according to rumors, AMD is currently working on processors having 256 cores each!
If you are confused about the difference between a processor and a core, or having trouble selecting a processor for your new build and cannot decide how many cores it ought to have, then this is the article for you.
Let us dig into the details of the different types of processor cores and their differences.
Table of contents
What is a Processor

A processor, also referred to as a Central Processing Unit (CPU), is a computing engine inside a device. In layman’s terms, it is the brain of the computer. It provides the processing power for the tasks to achieve them.
A processor is a miniature, logical circuit that performs the tasks delivered by different software. It is not necessary that a processor may have the same form factor as in the image above. For example, a mobile device’s processor may look something entirely different.
Initially, a processor was only designed with a single “core.” Over time, additional technologies were developed to improve its performance, including the following:
- Multiple Cores: Processor manufacturers, such as Intel and AMD, started to include multiple cores into a single silicon chip (a processor). This enabled each core to receive and perform individual tasks, simultaneously.
- Hyper-Threading: Hyper-threading, a technological term by Intel, is a core’s ability to receive and process 2 individual tasks simultaneously, virtually splitting a single core into two.
- Clock Speed: Each processor has a clock speed. This is the number at which a processor processes a stream of data. The greater the clock speed, the faster a processor will be, increasing the system’s performance. Clock speeds range from a few MegaHertz to several GigaHertz.
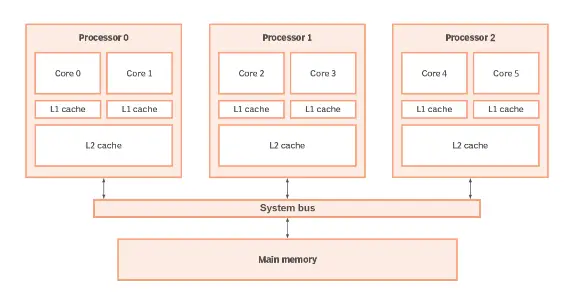
Some advanced systems have multiple processors embedded in them, each of them having multiple cores as well. this is done to maximize productivity and performance.
What is a Processor Core
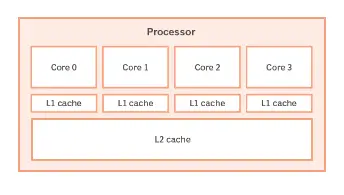
A processing core is a component that reads instructions and carries them out inside a processor. Most modern-day processors include multiple cores.
The commonly-available processors today can have cores anywhere between 2 and 24. The more cores, the merrier.
Each core can handle a different thread of data and process them at the same time. This results in faster loading times, less lag, and a greater overall user experience.
A core functions on the following 4 principles, which is known as the “instruction cycle“:
- Fetch: The processor core retrieves the awaiting instructions, typically from some type of memory.
- Decode: Each component of the fetched data has a feature known as an “opcode” that instructs the processor core what to do with the data that follows it. The various parts of the processor core can then begin working once the core has worked everything out.
- Execute: The processor now knows what needs to be done and actually performs the task at hand.
- Writeback: At this stage, the core moves the processed data back to where it should go.
All of this is done in one instruction cycle. Now imagine a ridiculously-fast core with extreme clock rates, and the processor has multiple cores to handle multiple threads at the same time. It would result in an absurd amount of data being processed in the blink of an eye.
What is a Multi-Core Processor
“Multi” stands for more than one. A processor having more than one core will be considered a multi-core processor.
When a processor has multiple cores integrated into the chipset, they are usually designed differently. For example, an octa-core processor may have 4 e-cores, which are the low-powered cores designed to handle less critical tasks, and the other 4 would be p-cores, which are performance cores, designed to handle power-intensive tasks.
Hexadeca Core Processor
The hexadeca-core processors have 16 cores embedded in the silicon chipset.
Below are the recent currently-available hexadeca-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3950X | AMD | Ryzen 9 | 25 November 2019 | 3.5 GHz |
| i9-9960X | Intel | Core i9 | November 2018 | 3.1 GHz |
| i7-13700K | Intel | Core i7 | 20 October 2022 | 2.5 GHz 3.4 GHz |
| i7-13700KF | Intel | Core i7 | 20 October 2022 | 2.5 GHz 3.4 GHz |
| PRO 5955WX | AMD | Ryzen Threadripper | 8 March 2022 | 4 GHz |
| i9-12900K | Intel | Core i9 | 4 November 2021 | 3.2 GHz |
| i9-12900KF | Intel | Core i9 | 4 November 2021 | 3.2 GHz |
| 73F3 | AMD | EPYC | 15 March 2021 | 3.5 GHz |
| 7313P | AMD | EPYC | 15 March 2021 | 3 GHz |
| 7313 | AMD | EPYC | 15 March 2021 | 3 GHz |
| AL73400 | Annapurna Labs | Alpine | 27 November 2018 | 2 GHz |
| CN9960 | Cavium | ThunderX2 | 7 May 2018 | 1.6 GHz 1.8 GHz 2 GHz 2.2 GHz |
| FT-1500A/16 | Phytium | FeiTeng | 26 July 2016 | 1.5 GHz |
| Hi1610 | HiSilicon ARM Holdings | Hi16xx | 2015 | 2.1 GHz |
| CN5860-1000 EXP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5860-1000 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5860-600 SCP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5860-800 EXP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
| CN5860-900 EXP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5860-600 EXP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5860-900 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5860-900 SCP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5860-600 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5860-800 SCP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
Tetradeca Core Processor
The tetradeca-core processors have 14 cores embedded in the silicon chipset.
Below are the recent currently-available tetradeca-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i5-13600KF | Intel | Core i5 | 20 October 2022 | 2.6 GHz, 3.5 GHz |
| i5-13600K | Intel | Core i5 | 20 October 2022 | 2.6 GHz, 3.5 GHz |
| i9-9990XE | Intel | Core i9 | 3 January 2019 | 4 GHz |
| i9-9940X | Intel | Core i9 | November 2018 | 3.3 GHz |
| D-2177NT | Intel | Xeon D | 7 February 2018 | 1.9 GHz |
| D-2173IT | Intel | Xeon D | 7 February 2018 | 1.7 GHz |
| W-2170B | Intel | Xeon W | 21 December 2017 | 2.5 GHz |
| i9-7940X | Intel | Core i9 | 25 September 2017 | 3.1 GHz |
| W-2175 | Intel | Xeon W | 29 August 2017 | 2.5 GHz |
| 5117 | Intel | Xeon Gold | 11 July 2017 | 2 GHz |
| 5119T | Intel | Xeon Gold | 11 July 2017 | 1.9 GHz |
| 5117F | Intel | Xeon Gold | 11 July 2017 | 2 GHz |
| 5120 | Intel | Xeon Gold | 11 July 2017 | 2.2 GHz |
| 5120T | Intel | Xeon Gold | 11 July 2017 | 2.2 GHz |
| 6132 | Intel | Xeon Gold | 11 July 2017 | 2.6 GHz |
| E5-2660 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 2 GHz |
| E5-2650L v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 1.7 GHz |
| E5-2670 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 3.1 GHz |
| E5-2658 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 2.3 GHz |
| E5-2680 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 2.4 GHz |
| E5-4628L v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 1.8 GHz |
| E5-2690 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 2.6 GHz |
| E5-4650 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 2.2 GHz |
| E5-2648L v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 1.8 GHz |
Dodeca Core Processor
The dodeca-core processors have 12 cores embedded in the silicon chipset.
Below are the recent currently-available dodeca-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i9-7920X | Intel | Core i9 | 28 August 2017 | 2.9 GHz |
| i9-9920X | Intel | Core i9 | November 2018 | 3.5 GHz |
| PRO 5945WX | AMD | Ryzen Threadripper | 8 March 2022 | 4.1 GHz |
| i7-12700K | Intel | Core i7 | 4 November 2021 | 3.6 GHz |
| i7-12700KF | Intel | Core i7 | 4 November 2021 | 3.6 GHz |
| 5900 | AMD | Ryzen 9 | 12 January 2021 | 3 GHz |
| 5900X | AMD | Ryzen 9 | 5 November 2020 | 3.7 GHz |
| PRO 3945WX | AMD | Ryzen Threadripper | 14 July 2020 | 4 GHz |
| 3900XT | AMD | Ryzen 9 | 7 July 2020 | 3.8 GHz |
| 4214R | Intel | Xeon Silver | 24 February 2020 | 2.4 GHz |
| fsd chip | Tesla | 10 March 2019 | 2.2 GHz | |
| CN5750-900 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5750-1000 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5750-900 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5750-1000 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5750-800 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
| CN5750-600 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5750-600 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5750-800 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
| CN5850-600 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5850-900 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
Deca Core Processor
A deca-core processor has 10 cores, or 10 physical CPUs, integrated into the chipset.
The most talked-about deca-core processor is MediaTek’s Helios X20 since it was one of the early birds. Below are the recent currently-available deca-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-2150B | Intel | Xeon W | 21 December 2017 | 3 GHz |
| i9-9820X | Intel | Core i9 | November 2018 | 3.3 GHz |
| i9-9900X | Intel | Core i9 | November 2018 | 3.5 GHz |
| i5-12600KF | Intel | Core i5 | 4 November 2021 | 3.7 GHz |
| i5-12600K | Intel | Core i5 | 4 November 2021 | 3.7 GHz |
| 4210R | Intel | Xeon Silver | 24 February 2020 | 2.4 GHz |
| 5215L | Intel | Xeon Gold | 2 April 2019 | 2.5 GHz |
| 5215M | Intel | Xeon Gold | 2 April 2019 | 2.5 GHz |
| 5215 | Intel | Xeon Gold | 2 April 2019 | 2.5 GHz |
| 4210 | Intel | Xeon Silver | 2 April 2019 | 2.2 GHz |
| Helio X30 | MediaTek ARM Holdings | Helio | 27 February 2017 | 2.5 GHz, 2.2 GHz, 1.9 GHz |
| Helio X27 | MediaTek ARM Holdings | Helio | 2 December 2016 | 2.6 GHz, 2 GHz, 1.6 GHz |
| Helio X23 | MediaTek ARM Holdings | Helio | 2 December 2016 | 2.3 GHz, 1.85 GHz, 1.4 GHz |
| Helio X20 M | MediaTek ARM Holdings | Helio | 16 March 2016 | 2 GHz, 1.85 GHz, 1.4 GHz |
| Helio X20 | MediaTek ARM Holdings | Helio | 16 March 2016 | 1.85 GHz, 1.4 GHz, 2.1 GHz |
| Helio X25 | ARM Holdings MediaTek | Helio | 16 March 2016 | 2.5 GHz, 2 GHz, 1.55 GHz |
| CN5745-900 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5745-600 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5745-800 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
| CN5745-900 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5745-1000 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5745-1000 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5745-600 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5745-800 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
Octa Core Processor
Octa means eight. All processors that have 8 cores fall into this category. Usually, octa-core processors are made up of two sets of quad-core setups. This allows them to process the data rather quickly by receiving it through separate threads.
Below is a list of the recent currently-available deca-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2700 | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 19 April 2018 | 3.2 GHz |
| PRO 1700 | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 3 GHz | |
| W-2140B | Intel | Xeon W | 21 December 2017 | 3.2 GHz |
| PRO 1700X | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 3.4 GHz | |
| i7-9800X | Intel | Core i7 | November 2018 | 3.8 GHz |
| PRO 5750G | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 1 June 2021 | 3.8 GHz |
| PRO 5750GE | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 1 June 2021 | 3.2 GHz |
| 5700GE | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 13 April 2021 | 3.2 GHz |
| 5700G | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 13 April 2021 | 3.8 GHz |
| 4980U | AMD | Ryzen 7 | 13 April 2021 | 2 GHz |
| S2 | Xiaomi ARM Holdings | Surge | ||
| Baikal-M | ARM Holdings | 2017 | 2 GHz | |
| SDM865 | Qualcomm ARM Holdings | Snapdragon 800 | March 2020 | 2.42 GHz, 2.84 GHz, 2.11 GHz |
| 8cx | Qualcomm ARM Holdings | Snapdragon 800 | March 2019 | 1.8 GHz, 2.84 GHz, 3.02 GHz |
| 990 4G | HiSilicon ARM Holdings | Kirin | 6 September 2019 | 2.86 GHz, 1.86 GHz, 2.088 GHz |
| 1000L | MediaTek | Dimensity | 2020 | 2.2 GHz, 2 GHz |
| S1 | Xiaomi ARM Holdings | Surge | 1.4 GHz, 2.2 GHz | |
| 9610 | Samsung ARM Holdings | Exynos | October 2018 | 2.3 GHz, 1.7 GHz |
| SM6125 | Qualcomm ARM Holdings | Snapdragon 600 | 9 April 2019 | 1.8 GHz, 4.5 GHz |
| 980 | HiSilicon ARM Holdings | Kirin | 31 August 2018 | 2.6 GHz, 1.92 GHz, 1.8 GHz |
| CN5740-1000 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5740-900 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5740-900 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.9 GHz |
| CN5740-600 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5740-800 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
| CN5740-1000 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 1 GHz |
| CN5740-600 SSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5740-800 SP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | August 2007 | 0.8 GHz |
| CN5840-600 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 0.6 GHz |
| CN5840-1000 SCP | Cavium | OCTEON Plus | February 2007 | 1 GHz |
Hexa Core Processor
Hexa-core processors have 6 physical cores that work in conjecture to process the data stream as quickly as possible.
Below is a list of the recent currently-available hexa-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3500X | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 3.6 GHz | |
| W-2135 | Intel | Xeon W | 29 August 2017 | 3.7 GHz |
| 1600 | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 11 April 2017 | 3.2 GHz |
| i7-8670T | Intel | Core i7 | ||
| i5-8420 | Intel | Core i5 | ||
| 2600X | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 19 April 2018 | 3.6 GHz |
| i5-8550 | Intel | Core i5 | ||
| 2600 | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 19 April 2018 | 3.4 GHz |
| i5-8420T | Intel | Core i5 | ||
| i5-8650 | Intel | Core i5 | ||
| PRO 1600 | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 3.2 GHz | |
| i5-8650K | Intel | Core i5 | ||
| i7-8670 | Intel | Core i7 | ||
| PRO 5650G | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 1 June 2021 | 3.9 GHz |
| PRO 5650GE | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 1 June 2021 | 3.4 GHz |
| 5600GE | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 13 April 2021 | 3.4 GHz |
| 5600G | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 13 April 2021 | 3.9 GHz |
| 4680U | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 13 April 2021 | 2.1 GHz |
| PRO 5650U | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 16 March 2021 | 2.3 GHz |
| 5600H | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 12 January 2021 | 3.3 GHz |
| 5600U | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 12 January 2021 | 2.3 GHz |
| 5500U | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 12 January 2021 | 2.1 GHz |
| 5600HS | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 12 January 2021 | 3 GHz |
| V2516 | AMD | Ryzen Embedded | 10 November 2020 | 2.1 GHz |
| V2546 | AMD | Ryzen Embedded | 10 November 2020 | 3 GHz |
| 5600X | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 5 November 2020 | 3.7 GHz |
| A14 Bionic | Apple | Ax | October 2020 | |
| PRO 4650GE | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 21 July 2020 | 3.3 GHz |
| PRO 4650G | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 21 July 2020 | 3.7 GHz |
| 4600GE | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 21 July 2020 | 3.3 GHz |
| 4600G | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 21 July 2020 | 3.7 GHz |
| 3600XT | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 7 July 2020 | 3.8 GHz |
| PRO 4650U | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 7 May 2020 | 2.1 GHz |
| 4600HS | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 16 March 2020 | 3 GHz |
| 4600H | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 6 January 2020 | 3 GHz |
| 4600U | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 6 January 2020 | 2.1 GHz |
| 4500U | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 6 January 2020 | 2.3 GHz |
| PRO 3600 | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 30 September 2019 | 3.6 GHz |
| A13 Bionic | Apple | Ax | 20 September 2019 | |
| 3600 | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 7 July 2019 | 3.6 GHz |
| 3600X | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 7 July 2019 | 3.8 GHz |
| E-2246G | Intel | Xeon E | 27 May 2019 | 3.6 GHz |
| E-2276G | Intel | Xeon E | 27 May 2019 | 3.8 GHz |
| E-2286G | Intel | Xeon E | 27 May 2019 | 4 GHz |
| E-2226G | Intel | Xeon E | 27 May 2019 | 3.4 GHz |
| E-2276M | Intel | Xeon E | 27 May 2019 | 2.8 GHz |
| E-2236 | Intel | Xeon E | 27 May 2019 | 3.4 GHz |
| i5-9500F | Intel | Core i5 | 23 April 2019 | 3 GHz |
| i5-9500T | Intel | Core i5 | 23 April 2019 | 2.2 GHz |
| i5-9400T | Intel | Core i5 | 23 April 2019 | 1.8 GHz |
| i5-9500 | Intel | Core i5 | 23 April 2019 | 3 GHz |
| i7-9750H | Intel | Core i7 | 23 April 2019 | 2.6 GHz |
| i5-9600 | Intel | Core i5 | 23 April 2019 | 3.1 GHz |
| i7-9850H | Intel | Core i7 | 23 April 2019 | 2.6 GHz |
| D-1633N | Intel | Xeon D | 2 April 2019 | 2.5 GHz |
| D-1637 | Intel | Xeon D | 2 April 2019 | 2.9 GHz |
| 3204 | Intel | Xeon Bronze | 2 April 2019 | 1.9 GHz |
| i5-9400 | Intel | Core i5 | 7 January 2019 | 2.9 GHz |
| i5-9400F | Intel | Core i5 | 7 January 2019 | 2.9 GHz |
| i5-9600KF | Intel | Core i5 | 7 January 2019 | 3.7 GHz |
| i5-9600K | Intel | Core i5 | 19 October 2018 | 3.7 GHz |
| A12 Bionic | Apple | Ax | 21 September 2018 | |
| 2600E | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 10 September 2018 | 3.1 GHz |
| PRO 2600 | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 6 September 2018 | 3.4 GHz |
| E-2176G | Intel | Xeon E | 12 July 2018 | 3.7 GHz |
| E-2146G | Intel | Xeon E | 12 July 2018 | 3.5 GHz |
| E-2186G | Intel | Xeon E | 12 July 2018 | 3.8 GHz |
| E-2126G | Intel | Xeon E | 12 July 2018 | 3.3 GHz |
| E-2136 | Intel | Xeon E | 12 July 2018 | 3.3 GHz |
| i7-8086K | Intel | Core i7 | 8 June 2018 | 4 GHz |
| E-2186M | Intel | Xeon E | 2 April 2018 | 2.9 GHz |
| i9-8950HK | Intel | Core i9 | 2 April 2018 | 2.9 GHz |
| i5-8500T | Intel | Core i5 | 2 April 2018 | 2.1 GHz |
| i7-8750H | Intel | Core i7 | 2 April 2018 | 2.2 GHz |
| i7-8700B | Intel | Core i7 | 2 April 2018 | 3.2 GHz |
| i5-8600 | Intel | Core i5 | 2 April 2018 | 3.1 GHz |
| i7-8700T | Intel | Core i7 | 2 April 2018 | 2.4 GHz |
| i5-8500 | Intel | Core i5 | 2 April 2018 | 3 GHz |
| i5-8400T | Intel | Core i5 | 2 April 2018 | 1.7 GHz |
| E-2176M | Intel | Xeon E | 2 April 2018 | 2.7 GHz |
| i7-8850H | Intel | Core i7 | 2 April 2018 | 2.6 GHz |
| i5-8500B | Intel | Core i5 | 2 April 2018 | 3 GHz |
| i5-8600T | Intel | Core i5 | 2 April 2018 | 2.3 GHz |
| i5-8400B | Intel | Core i5 | 2 April 2018 | 2.8 GHz |
| 7872 | Samsung ARM Holdings | Exynos | 17 January 2018 | 2 GHz, 1.5 GHz |
| i7-8700K | Intel | Core i7 | 5 October 2017 | 3.7 GHz |
| i7-8700 | Intel | Core i7 | 5 October 2017 | 3.2 GHz |
| i5-8600K | Intel | Core i5 | 5 October 2017 | 3.6 GHz |
| i5-8400 | Intel | Core i5 | 5 October 2017 | 2.8 GHz |
| A11 Bionic | Apple | Ax | 22 September 2017 | |
| W-2133 | Intel | Xeon W | 29 August 2017 | 3.6 GHz |
| 6128 | Intel | Xeon Gold | 11 July 2017 | 3.4 GHz |
| 3104 | Intel | Xeon Bronze | 11 July 2017 | 1.7 GHz |
| D-1533N | Intel | Xeon D | July 2017 | 2.1 GHz |
| i7-7800X | Intel | Core i7 | 26 June 2017 | 3.5 GHz |
| A10X Fusion | Apple | Ax | 13 June 2017 | |
| 1600X | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 11 April 2017 | 3.6 GHz |
| E5-1650 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 3.6 GHz |
| E5-2643 v4 | Intel | Xeon E5 | 20 June 2016 | 3.4 GHz |
Quad Core Processor
A quad-core processor has 4 cores inside of it. Each of those cores functions independently to process a data string.
Below is a list of the recent currently-available quad-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i3-8020T | Intel | Core i3 | ||
| i7-8550U | Intel | Core i7 | 21 August 2017 | 1.8 GHz |
| W-2104 | Intel | Xeon W | 29 August 2017 | 3.2 GHz |
| i3-8320 | Intel | Core i3 | 3.8 GHz | |
| i5-8365U | Intel | Core i5 | 16 April 2019 | 1.6 GHz |
| i7-8709G | Intel | Core i7 | 7 January 2018 | 3.1 GHz |
| i3-9000T | Intel | Core i3 | 3.2 GHz | |
| i7-8650U | Intel | Core i7 | 21 August 2017 | 1.9 GHz |
| i3-8320T | Intel | Core i3 | ||
| i5-8305G | Intel | Core i5 | 7 January 2018 | 2.8 GHz |
| i3-9000 | Intel | Core i3 | 3.7 GHz | |
| i3-8120 | Intel | Core i3 | 3.7 GHz | |
| i5-8250U | Intel | Core i5 | 21 August 2017 | 1.6 GHz |
| i5-8350U | Intel | Core i5 | 21 August 2017 | 1.7 GHz |
| PRO 1300 | AMD | Ryzen 3 | 3.5 GHz | |
| i7-8706G | Intel | Core i7 | 7 January 2018 | 3.1 GHz |
| i3-8120T | Intel | Core i3 | 3.2 GHz | |
| 1400 | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 11 April 2017 | 3.2 GHz |
| i3-8020 | Intel | Core i3 | ||
| i5-8265U | Intel | Core i5 | 28 August 2018 | 1.6 GHz |
| W-2102 | Intel | Xeon W | 29 August 2017 | 2.9 GHz |
| PRO 1200 | AMD | Ryzen 3 | 3.1 GHz | |
| 1500X | AMD | Ryzen 5 | 11 April 2017 | 3.5 GHz |
| i7-8705G | Intel | Core i7 | 7 January 2018 | 3.1 GHz |
| PRO 5350G | AMD | Ryzen 3 | 1 June 2021 | 4 GHz |
Dual Core Processor
As the name suggests, dual-core processors have a total of 2 physical cores. This technology is somewhat outdated and may only be found in older computers.
Below is a list of the currently-available dual-core processors in the market:
| Model | Manufacturer | Family | Launched | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i3-7120T | Intel | Core i3 | 3.5 GHz | |
| i5-7210U | Intel | Core i5 | 2.5 GHz | |
| i3-7320T | Intel | Core i3 | 3.6 GHz | |
| i3-7110U | Intel | Core i3 | 2.6 GHz | |
| i3-7340 | Intel | Core i3 | 4.2 GHz | |
| 3965Y | Intel | Celeron | 1.3 GHz | |
| i3-7007U | Intel | Core i3 | 2.1 GHz | |
| i3-7310U | Intel | Core i3 | 2.7 GHz | |
| M3-8114Y | Intel | Core M3 | 1.5 GHz | |
| i3-7120 | Intel | Core i3 | 4 GHz | |
| 9110 | Samsung, ARM Holdings | Exynos | 9 August 2018 | |
| 7270 | Samsung, ARM Holdings | Exynos | November 2016 | 1 GHz |
| V2H | Renesas, ARM Holdings | R-Car | October 2016 | 1 GHz |
| a9 | Apple | Ax | 25 September 2015 | 1.85 GHz |
| a7 | Apple | Ax | 20 September 2013 | 1.4 GHz |
| a6 | Apple | Ax | 21 September 2012 | 1.3 GHz |
| M1A | Renesas, ARM Holdings | R-Car | June 2012 | 0.8 GHz |
| 5250 | Samsung, ARM Holdings | Exynos | 30 November 2011 | 1.7 GHz |
| 4212 | Samsung, ARM Holdings | Exynos | 29 September 2011 | 1.5 GHz |
| 4210 | Samsung, ARM Holdings | Exynos | 17 June 2011 | 1.4 GHz |
| Baikal-T1 | Baikal Electronics, Imagination Technologies | February 2016 | 1.2 GHz | |
| CN3120-400 EXP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.4 GHz |
| CN3120-550 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.55 GHz |
| CN3120-400 SCP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.4 GHz |
| CN3120-300 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.3 GHz |
| CN3120-500 CP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.5 GHz |
| CN3120-500 SCP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.5 GHz |
| CN3120-550 EXP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.55 GHz |
| CN3120-500 NSP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.5 GHz |
| CN3120-300 SCP | Cavium | OCTEON | 1 May 2006 | 0.3 GHz |
Multi-Core Processor Considerations
When selecting a computer or even an individual processor, there are a few considerations that you need to make before investing your money in it.
Type of Work
The first and most important consideration to make is what type of work you’ll be performing atop the processor. Will it be CPU-intensive, like graphic designing and image rendering, or will you only use it to edit your daily files or folders?
If you plan on using it for day-to-day tasks, like editing an Excel sheet, then a dual or quad-core processor with a good clock speed may do the trick. However, if you are looking to play graphics-intensive games on the computer, then you may want to have an octa or deca-core processor.
Power Consumption
Another significant factor that should impact your decision is power consumption. Will be mostly on the go and not have frequent access to a power outlet, or do you plan on being always plugged in?
If you want your laptop’s or phone’s battery to last longer, then you may want to choose a device with fewer cores, as the more cores there are, the faster your battery will drain.
At this point, you may also want to glance at the core types. Are they all P-cores, or are their low-powered cores available on the chipset as well?
Heat Dissipation
The hat dissipation of a device is often overlooked. You need to make sure that your device will dissipate the heat as quickly as it generates it.
More processing cores working in conjecture will mean more heat is produced. Therefore, you must be prepared to compensate for the extensive heat with cooling fans, liquid-cooled radiators, or other means.
If you choose a dual or quad-core processor, then heat management would be easier and more cost-effective.
Multitasking
Do you plan on running 10 or more applications at the same time? If so, then you must go for the deca-core processors. The more cores there are, the more data threads your processor could handle simultaneously.
This, in turn, will increase your system’s performance, and hence, your productivity.
Of course, a decision cannot be made on multitasking alone. You must also consider the factors we have discussed above, like heat dissipation and power consumption.
If you run maybe 5-6 apps at a time, then even a good quad-core processor might fulfill your needs.
Costs
Your budget is where it all comes to a halt. It will cost you more as you go higher up the ladder in terms of processor cores.
Processors with a lower number of cores are relatively cheaper and abundantly available, whereas finding a processor with 10 or 12 cores might need some homework first.
At this point, consider again what you will be doing with a processor if you choose one, and whether it is worth the price.
Are More Processor Cores Good?
It goes without saying; the more cores your processor has, the better performance it will give. Since it is then able to process more threads at the same time.
However, we would like to add that you must also take into consideration the points that we have discussed above, like heat dissipation, costs, and power consumption.
Do You Need a Deca Core Processor?
Deca-core processors, or even octa-core ones, are sufficient for any vivid gamers, given that there isn’t another bottleneck on the system. You may also want a deca-core processor if you are a 3-D animator, or perform any sort of image and video rendering.
However, if you have no dedicated goal of what you will do with your new PC or processor, then we recommend that you do not get a deca-core processor right now. Instead, go for a quad or a hexa-core, since those are sufficient to perform daily average tasks.
How to Check Number of Processor Cores
If you want to check how many physical and virtual cores your current processor has, here are the steps (for Windows PC):
-
Open the Task Manager by pressing the CTRL + Shift + Esc hotkeys.
-
Switch to the Performance tab and select “CPU.”
-
View the “Cores” and the “Logical processors” in the details.
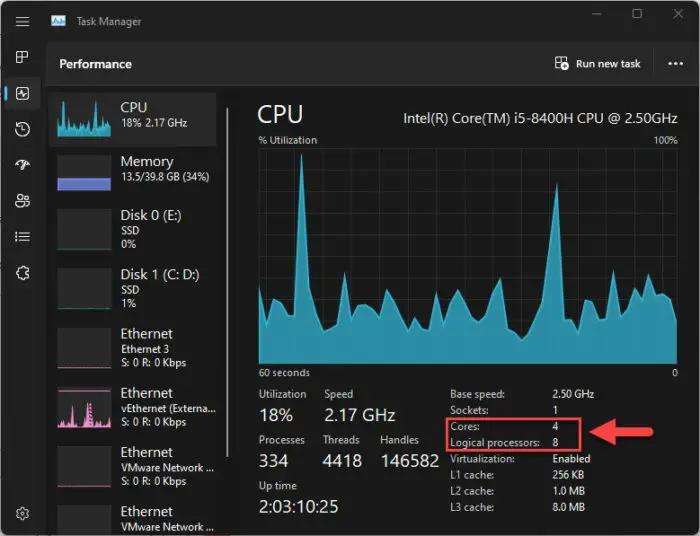
View physical and virtual processor cores
Takeaway
The number of processor cores makes all the difference in your system’s performance. It is true that the more cores you have, the greater your computer or phone will perform, and the more responsive it will be. However, there are other things you must also consider before “going big.”
In conclusion, you should get a device with a processor that meets your needs, with a little extra legroom to compensate for any unforeseen workloads that may befall you.