Microsoft has now released Windows PowerShell versions 7.0.11 and 7.2.4. PowerShell is a scripting and automation Windows command-line tool that you can upgrade to the said versions with several fixes and improvements.
Although PowerShell 7 Preview 3 was released a while back, which is the latest PowerShell version at the time of writing this post, we do not recommend you install it in a production environment. Instead, you should install stable versions, like this one.
Both of these releases are Long-Term Servicing (LTS) channels, which means they will receive support until the end-of-support for .NET. The LTS release only receives critical security updates and servicing fixes designed to minimize the impact on existing workloads.
You can download and install the respective versions from the direct download links below and install them.
Table of contents
Download PowerShell 7.0.11
For Windows
PowerShell-7.0.11-win-x64.msi [87.8 MB]
PowerShell-7.0.11-win-x86.msi [79.8 MB]
For MacOS
PowerShell-lts-7.0.11-osx-x64.pkg [55.5 MB]
For Linux
CentOS
PowerShell-lts-7.0.11.centos.8.x86_64.rpm [55.4 MB]
Debian
PowerShell-lts-7.0.11.debian.11_amd64.deb [55.8 MB]
PowerShell-lts-7.0.11.debian.10_amd64.deb [55.8 MB]
Ubuntu
PowerShell-lts-7.0.11.ubuntu.20.04_amd64.deb [55.8. MB]
PowerShell-lts-7.0.11.ubuntu.18.04_amd64.deb [55.8 MB]
PowerShell-lts-7.0.11.ubuntu.16.04_amd64.deb [55.8 MB]
For more download options, please check out this download page.
Download PowerShell 7.2.4
For Windows
PowerShell-7.2.4-win-x64.msi [102 MB]
PowerShell-7.2.4-win-x86.msi [93.3 MB]
For MacOS
PowerShell-lts-7.2.4-osx-x64.pkg [63.7 MB]
For Linux
PowerShell-7.2.4-linux-x64.tar.gz [66.2 MB]
PowerShell-7.2.4-linux-arm64.tar.gz [61.8 MB]
PowerShell-7.2.4-linux-arm32.tar.gz [63.2 MB]
PowerShell-lts_7.2.4-1.deb_amd64.deb [66.2 MB]
For more download options, please check out this download page.
Let us now see the improvements in each of these PowerShell versions.
Fixes and Improvements
PowerShell 7.0.11
- Add explicit job name for approval tasks in the Snap stage.
- Update to use
mcr.microsoft.com. - Update global.json and Wix.
- Put Secure supply chain analysis in the correct place.
- Partial back-port of: Update a few tests to make them more stable in CI.
- Replace . in the notices container name.
- Add an approval for releasing build-info JSON.
- Release build info JSON when it is a preview.
- Add a major-minor build info JSON file.
- Update release instructions with link to new build.
- Add a condition to generate release files in local dev build only.
- Removed old not-used-anymore docker-based tests for PS release packages.
- Publish the global tool package for stable releases.
- Update to use
windows-latestas the build agent image. - Don’t upload
depor<a href="https://www.itechtics.com/open-tar-gz-tar-gz-tgz-files/" data-type="post" data-id="66106">tar.gz</a>forRPMbuild because there are none. - Update to
vPacktask version 12. - Make RPM license recognized.
- Ensure
psoptions.jsonandmanifest.spdx.jsonfiles always exist in packages.
PowerShell 7.2.4
- Add mapping for Ubuntu22.04 Jammy.
- Update to use
mcr.microsoft.com. - Update third-party notices.
- Update global.json and Wix.
- Put Secure supply chain analysis in the correct place.
- Fix web cmdlets so that an empty
Getdoes not include acontent-lengthheader. - Update package fallback list for Ubuntu (from those updated for Ubuntu 22.04)
- Add sha256 digests to RPM packages.
- Allow multiple installations of .NET.
For more information, visit PowerShell support lifecycle.
How to Install PowerShell 7.0.11 or 7.2.4
Perform the following steps to install PowerShell on a Windows operating system:
-
Download and execute the respective MSI files from the links above.
-
The installation wizard will now run. Click Next on the first screen.
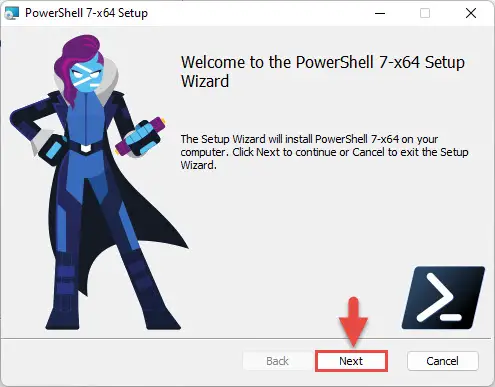
Click Next -
On the next screen, leave the default installation directory and click Next.
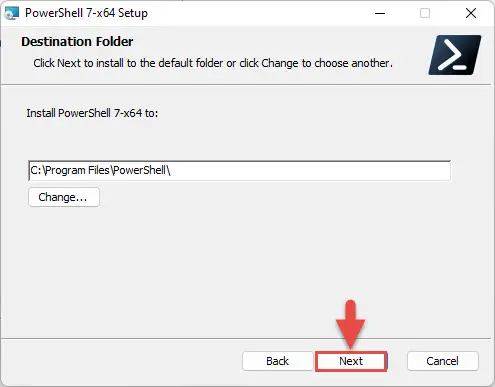
Click Next again -
Select the optional features you want to install, such as adding PowerShell to environment variables, enabling PowerShell remoting, adding PowerShell to the context menu, etc. Click Next when selected.
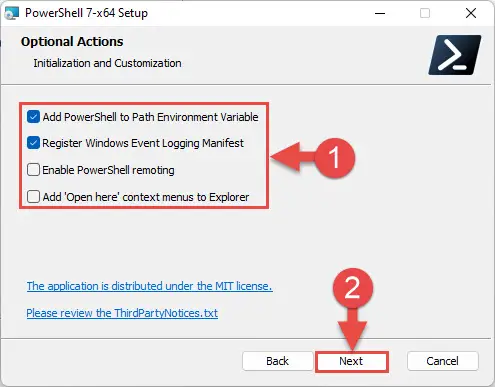
Select optional features -
On the next screen, click Install to begin the installation process.
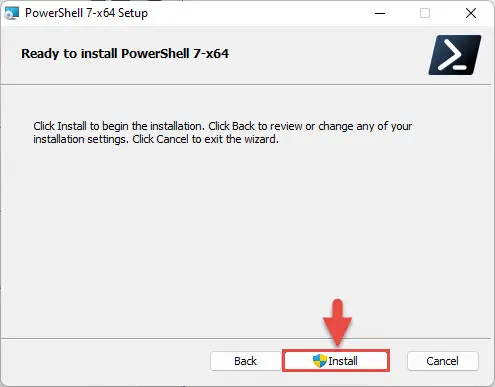
Begin installation -
Once installed, click Finish.
Complete installation -
Now confirm that PowerShell has been installed by running PowerShell. To do so, type in pwsh in the Run Command box. The PowerShell window will then open displaying the current version.
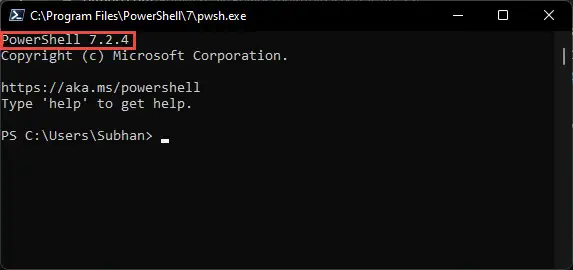
Confirm installation version
You can also install PowerShell 7.2.4 using the command line using the cmdlet given below. Make sure you run PowerShell as an administrator. This command is also useful when you want to upgrade from an older version of PowerShell to the latest version.
iex "& { $(irm https://aka.ms/install-powershell.ps1) } -UseMSI -Quiet"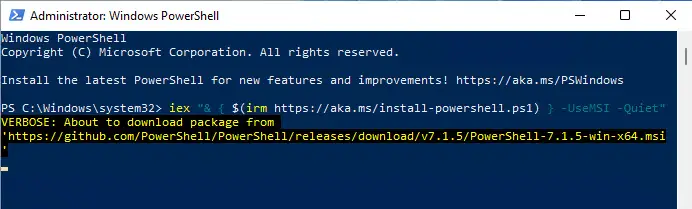
This will automatically install PowerShell 7.2.4 with the default options. You can also migrate from the default PowerShell 5 to PowerShell 7.2.4.
There is another option to install PowerShell over the network which is especially useful for sysadmins.



