With the use of network-connected technology at an all-time high, it is becoming increasingly important to protect both organizational as well as personal networks and devices. If your devices, like phones, tablets, and computers, are connected to the internet, they are prone to cyberattacks and hacking.
To protect such devices, firewalls are no longer sufficient. Although firewalls are becoming increasingly necessary, monitoring and controlling network traffic using firewalls alone is becoming difficult. This is where the Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems come in.
Intrusion detection is one part of the protection system, and prevention is another. These often come as separate protection technologies or are sometimes combined. Therefore, you may find “Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)“, “Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)“, and “Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)“, separately.
Whether you are a security professional, a parent, or just protective of your sensitive digital data, this article can help you understand the fundamentals of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems, their types, how they work, and how you can benefit from them
By the end of this article, you should be able to differentiate between an IDS and an IPS, and its types, and make an informed decision on what technology, as well as its type, is suitable for your networking infrastructure.
This page covers
What is IDS, IPS, IDPS?
What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)?
An IDS can be a hardware or software whose purpose is to monitor the network, device, or application traffic for malicious activity or threats and send out an alert to the administrator. It is used to detect irregular activity so that appropriate action can be taken to prevent it.
Depending on the type of IDS, it can also monitor application logs to check for threats and vulnerabilities and report them to the administrators. The alerts can be in the form of a notification or an email; whichever option has been configured.
In addition to the type of an IDS signified by its state (hardware or software), they are also categorized according to their detection methods. These have been discussed below in detail.
What is an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)?
An IPS is a slightly advanced version of the IDS. It does everything an IDS can, and more. An IPS monitors the traffic and detects potential threats before reporting them to the administrator. Additionally, an IPS can also take the appropriate action automatically to prevent the threat.
Note: When referring to the Intrusion Prevention System, the detection part is already implied.
For example, if an incident is detected, an IPS can cut off all communication with the internet unless normal traffic is restored.
Like the IDS, an IPS can be hardware or software. However, its functional methods are somewhat different from an IDS.
What is an Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)?
An IDPS includes the best of both worlds. It is usually a device, or software, that contains the functionality of both an IDS and an IPS. An IDPS is usually installed as a node from where all organizational traffic enters all leaves the network.
In simpler words, an IDPS detects and responds to cyber threats to report them and minimalize their impact; the same as an IPS. Therefore, the words “IPS” and “IDPS” are often used interchangeably.
IDS vs IPS
An IPS does everything an IDS does, and then some. This makes the IPS an even more advanced technology than an IDS, with more features. This often makes people believe that they do not need an IDS, and that only the implementation of an IPS will protect their network.
While that may be true, that is not always the case. Some organizations deploy both. this helps them send out an alert to the security professionals while the IPS blocks off the threat.
However, not all IPS responses are favorable for the company. For example, while there is a threat, a complete internet blockage of the entire organization may not be favorable. In this case, you may just want to alert the security professional using an IDS and not invoke any automated prevention systems, so that a human can take the appropriate countermeasures without shutting down the entire network.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
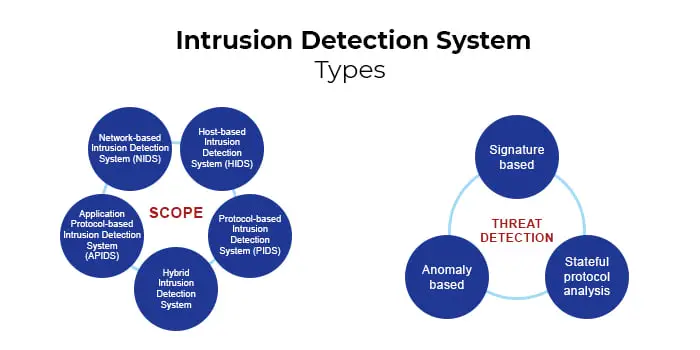
There are different types of IDS available in the market today. These can be hardware-based or software-based. Additionally, they can be categorized according to their scope or detection type.
Types of IDS based on scope
-
Network-based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
A NIDS is usually hardware, but can also be deployed using software and connecting it to the network.
NIDS monitors the complete network traffic and is normally installed from where all of the digital traffic leaves or enters the network. This way, it can monitor, detect, and report all malicious traffic entering or leaving the network.
NIDS are used to detect real-time, live threats so that appropriate action can be taken immediately. Moreover, they are ideal for packet-level inspection so all the headers and the payloads are scanned thoroughly.
-
Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS)
The Host-based IDS, as the name implies, is installed on the host, or an endpoint (computer). These are IDS software and monitor the logs created by other applications and programs to filter out any threats or irregular patterns.
HIDS are used to protect individual nodes throughout the network, such as servers and computers with sensitive data. However, these are used for passive security, since they can only monitor and detect irregular activity from previously-generated log files by other applications. However, instead of going through every log file individually, HIDS can be very helpful in filtering out malicious traffic and network patterns.
-
Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (PIDS)
PIDS are usually connected to the front of servers to monitor the protocols that are being used. For example, it can be used to analyze HTTP and HTTPS communication going to and from the server.
A PIDS sends out alerts to the administrator in case it detects that some other protocol is being used to communicate with the server, other than the one authorized.
-
Application Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (APIDS)
An Application Protocol-based IDS is similar to a PIDS, with the difference in the ability to monitor a group of servers, instead of just one. The main purpose of this type of IDS is to monitor, detect, and report any communication protocol abnormality in the traffic coming and going from a specific application.
-
Hybrid Intrusion Detection System
A hybrid IDS can be a combination of two or more types of Intrusion Detection Systems. You may find these in large-scale organizations that implement multiple levels of security to minimize the risk.
This concludes our take on the 5 types of IDS based on their scope. However, there is still more to them.
Types of IDS based on threat detection
Intrusion Detection Systems are also categorized based on their threat detection functionality. Here are the 3 main threat detection techniques that IDS uses:
-
Signature-based
The IDS running the signature-based detection mechanisms are like antiviruses if running on a host. They scan the logs for known keywords and patterns for predefined threats and send out alerts to the security administrators. Since the attack type is already known and already fed to the system, the administrators can take proper action to prevent it any further.
Similarly, a host-based IDS with a signature-based detection algorithm is like a firewall. It will block out all malicious data packets and prevent them from passing through to the target.
-
Anomaly-based
An IDS with an anomaly-based detection mechanism is more comprehensive than an IDS with a signature-based detection algorithm. This is because an anomaly-based IDS can detect new threats with malicious data and patterns, and is therefore ideal to report zero-day attacks. It uses shot or network-specific profiles to detect suspicious activity.
That said, an anomaly-based IDS can often report false positives, which means that even normal traffic can accidentally be reported as a threat.
-
Stateful protocol analysis
An IDS with stateful protocol analysis takes it a step further than an anomaly-based IDS. Stateful protocol analysis uses predefined standards of different communication protocols and cross-checks them against the observed traffic to check for deviations.
If it finds any deviations, it immediately reports the activity to the administrators.
Types of Intrusion Prevention Systems
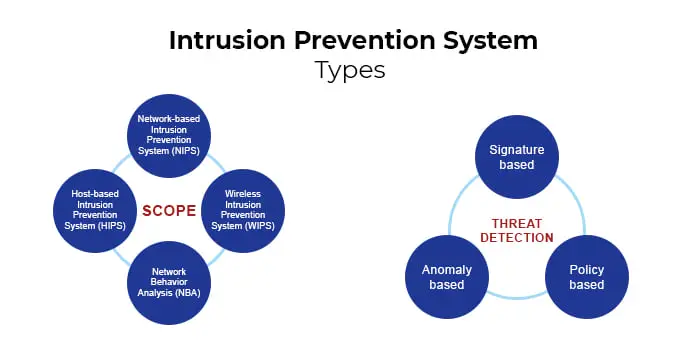
Like IDS, an IPS also has different types. They, too, can be categorized using both their scope and their detection and prevention techniques.
Types of IPS based on scope
-
Network Intrusion Prevention System (NIPS)
A Network Intrusion Prevention System is normally deployed at strategic endpoints within a network, usually from where all traffic passes, like behind firewalls, routers, etc.
Similar to NIDS discussed above, NIPS monitor and detect all the data packets passing through and block all data that matches the predefined database of known attacks. Since it is a “prevention” technology, it can be configured to perform certain actions, such as blocking the packets or cutting off the internet, and not only detect and report the incident like an IDS.
-
Host Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS)
A HIPS is installed on a host, normally a critical server, which needs automatic protection from cyber threats. However, unlike a HIDS, the HIPS monitors the network traffic coming to and from that particular device, instead of monitoring the log files. Therefore, a HIPS is considered real-time protection software.
When a Host Intrusion Prevention System detects an anomaly, it not only reports it but also blocks the malicious traffic from doing any damage.
-
Network Behavior Analysis (NBA)
Like NIPS, an NBA also monitors traffic patterns to detect and block malicious traffic. However, instead of monitoring the protocol activity, NBA detects unusual network traffic. These patterns usually result from policy violations, malware attacks, or DDoS attacks.
NBA IPS can be installed at locations to monitor external traffic, as well as internal traffic, to prevent malicious attacks from the inside.
-
Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS)
As the name implies, Wireless IPS is used to prevent unauthorized wireless access to networks. Such systems monitor and cross-check the wireless networking protocols in use against predefined datasets and check for anomalies.
A WIPS usually just kicks off unauthorized devices connected to a Wi-Fi network.
Types of IPS based on threat prevention
Like IDS, IPS can also be categorized according to its prevention algorithm.
-
Signature-based
Known threats and attacks have a specific pattern that is already recorded. A signature-based IPS monitors the live traffic and compares it to the predefined pattern, referred to as a signature, and blocks the incoming or outgoing traffic which matches a threat’s description.
Unlike the signature-based IDS, the IPS can take action automatically and prevent a cyber incident from occurring.
-
Anomaly-based
Like an anomaly-based IDS, an IPS is capable of blocking new, zero-day threats by detecting irregular traffic patterns. It can determine whether the network traffic is malicious or not by comparing it to a baseline standard. If they do not match, the traffic is automatically blocked.
That said, it can sometimes produce a false positive and block certain network traffic which is not malicious, but simply doesn’t match the baseline standards.
-
Policy-based
Policy-based IPS is where an organization of security professionals defines its own set of rules, and any data packets violating those rules are automatically blocked.
Although uncommon, policy-based IPS is very much possible. However, it does require an expert to be able to configure and define the custom policies.
This concludes all the types of IDS and IPS that are used by different organizations and firms. But one thing still remains – why are Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems even used when there are other security mechanisms in place, like firewalls and antivirus software?
Why are Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems used?
Firewalls and antivirus software are very limited in their capacity. While they may block certain levels of threats and attacks, they may not be able to detect them right away. For example, when a certain attack is relatively new and a software’s signature database has not been updated, it will not detect or prevent the attack.
This is why Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems are considered smart. They are programmed to detect anomalies based on standard thresholds and automatically perform the necessary actions to block an attack.
If you already have other security checks in place, here is why you may want to consider adding an IDPS to the existing network:
- Enhanced security: An IDPS can work in tandem without security checks in place, and detect and prevent malicious activities which other technologies can’t.
- Instant response: Rather than wasting time on human response and manual configurations, an IPS can instantly block an attack automatically without having to endure any damage.
- Save time: IDPS are largely automated and require very limited user input.
- Framework compliance: An IDPS satisfies many of the security framework compliance requirements and provides auditing guidelines.
- Customization options: Organizations and security experts can configure IDPS to set when to send out alerts, what prevention techniques to apply, and much more.
Takeaway
IDS and IPS are both the same and very different. While both of them are available in hardware and software, and both of them monitor the network traffic and logs, they both do not respond alike. While an IDS is only capable of sending out alerts, an IPS is capable of taking the appropriate action without human involvement and preventing an ongoing cyberattack.
With evolving technology, so is the sophistication of cyberattacks. The use of IDS, IPS, and IDPS is becoming more and more of a necessity. It is now critical that you protect your assets, network, and all sensitive data from all sorts of threats and incorporate advanced security protection devices, like IDPS and NGFWs, into your networks.
That said, it is not sufficient to install only an IDS, IPS, or an IDPS while leaving out all the other parts of the security framework. While an IPS may just work fine, at least initially, only a single point of failure is not worth risking everything within the network. Moreover, this will put all of the security monitoring load on a single device, wearing it out, and eventually leading to an early breakdown.




