DDR4 is the fourth generation RAM technology after DDR3. DDR means Double Data Rate. DDR3 and DDR4 are types of RAMs that can’t be compared easily because both need different kinds of hardware to operate. But we will try to compare the functionality of both RAM types in easy and plain language so that everyone can understand the core differences between the two and decide whether to upgrade or not.
When we look at the market share of both types of RAMs, DDR4 is not backward compatible and is only available for Intel’s X99 platform. One interesting thing to note here is that DDR4 does not give a performance boost for Gaming PCs.
Before we dig into the key differences, let us give you a glimpse of their comparison:
| DDR3 | DDR4 | |
| Release Year | 2007 | 2014 |
| Speed | 800MHz-2133MHz | 1600MHz-3200MHz |
| Bandwidth | 12.8GB/s | 21.3GB/s |
| Latency | Slightly lower than DDR4 | Negligibly higher than DDR3 |
| Power Consumption | 1.5V (1.35 with power-saving) | 1.2V |
| Capacity | 128GB (4 dyes) | 512GB (8 dyes) |
| Error-Handling | Less efficient than DDR4 | Better detection, prevention, correction |
Let’s go through the comparison bit by bit and then conclude at the end.
Voltage and Power Usage
DDR3 operates on 1.5V (1.35V on power-saving mode) while DDR4 operates on 1.2V. This means that DDR4 RAM will use a lot less power as compared to DDR3. On only one or two systems, this doesn’t make much of a difference but on the server side, if there are hundreds of servers running the same hardware, upgrading the RAM to DDR4 will make quite a visible difference in power usage of the whole environment.
Speed and Bandwidth
The frequency of DDR3 starts at 800 MHz and ends at 2133 MHz. 800 MHz means the RAM has a speed of 800 million operations per second. DDR4 memory starts at 1600 MHz and goes up to 3200 MHz. This increase in frequency implies the increased bandwidth of RAM. So DDR4 is capable of much more bandwidth than DDR3.
The downside of higher frequency is higher latency. Although there is not much of a difference, what DDR4 lacks in latency makes up for in bandwidth. All-in-all, DDR4 compensates in performance well-above DDR3 despite its higher latency.
You can learn more about frequency and latency in this video:
Capacity and Error Handling
If it comes to the biggest visible difference between DDR3 and DDR4, I will vouch for the capacity. DDR4 is able to have a much higher RAM capacity as compared to DDR3. DDR3 supports 4 dyes per module while DDR4 supports 8 dyes per module.
The theoretical maximum capacity of DDR3 RAM is about 128 GB while DDR4 RAM can go up to 512 GB. This is a huge improvement especially when we have limited RAM slots.
In addition to huge capacity, DDR4 memory is capable of much better error detection, prevention, and correction. Error handling becomes very important when there is a large capacity of memory installed in a system and the system is handling some real-time operations like satellites, traffic systems, etc.
The Design Differences
The physical design of DDR4 is a little different as compared to DDR3 memory. Here is the screenshot of each RAM slot:
DDR3 vs DDR4:
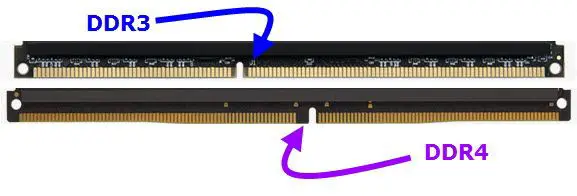
Not all hardware supports both kinds of RAMs, and the motherboard does the trick for you, as it only allows the supported RAM modules by adjusting the slit’s location in the memory bus.
The Real-World Conclusion
Most latest devices have shifted to DDR4 and the associated hardware, such as the motherboard and the CPU also support DDR4 only. DDR5 has also been launched recently with much higher specifications than DDR4. However, DDR4 still holds a dominant position in the market as DDR5 has still in its early development stages, and DDR3 has been outdated as it is not supported by the latest CPUs or motherboards.
What are your thoughts about DDR4 RAM? Did I miss anything in this difference between DDR3 and DDR4 in easy language? Please share your thoughts in the comments below.






2 comments
ANIL ROUTH
I want to know about processors with generation wise in a simple way
Windows10Geek
Pretty good comparison. I would have loved if you covered latency and frequency in detail. Another thing missing is uncovering DDR. DDR is double data rate which means that the actual data rate of RAM is half the advertised rate. For example, I have a 1600 MHz DDR3 RAM in my computer. So the actual physical bandwidth of my RAM would be 800MHz! But since my RAM can carry two packets in each transfer/cycle, the actual bandwidth which my RAM module can handle is doubled. Hence it’s called Double Data Rate :)